What Are Prime Numbers?
Learn the definition of prime numbers, how we use them in math and see a list of prime numbers up to 100.

Author
Tess Loucka
Published:
November 2024
Key takeaways
- • A prime number is any positive number that can only be divided by itself and the number 1.
- • There are 25 prime numbers up to 100: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97.
- • The opposite of prime numbers are composite numbers. Composite numbers have more than two factors.
Prime numbers are one of the most important building blocks in all of mathematics, and the foundation of countless mathematical discoveries throughout the centuries.
The idea of prime numbers dates back to around 1550 BC with the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus from ancient Egypt. However, the first definitive study of prime numbers took place in ancient Greece in the 300s BC when Greek mathematician, Euclid, made a clear distinction between prime and composite numbers and proved the infinitude of prime numbers.
His discoveries became the basis of math as we know it!
Today, prime numbers are used in encryption and decryption software, rotor machines, telecommunication codes, and hash tables that organize and display data.
Primality, or the property of being prime, is integral to so many areas of math and real life situations. But, what is a prime number?
Prime Number Definition
A prime number is any positive number that can only be divided by itself and the number 1. That is the most basic prime number definition.
Take 3 for example. Three is only divisible by 1 and 3. That makes 3 a prime number!
Let’s look at the number 6 now. Six is divisible by 1, 6, 2, and 3. It has four factors, meaning it is not a prime number.
You can quickly figure out what a number’s factors are by using a multiplication square.
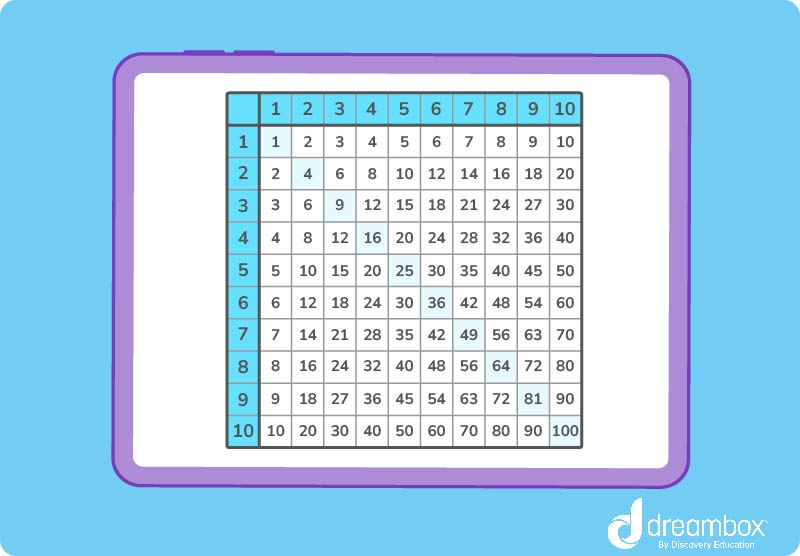
Properties of Prime Numbers
If you’re ever unsure if a number is prime, look at the list of prime number properties below.
- It’s only divisible by itself and the number 1
This is the classic definition of prime numbers and the first thing you should look for when figuring out if a number is prime.
- It’s a positive number
Prime numbers are always positive because positive numbers are the only numbers that can have only two factors. 3 has two factors, 1 and 3. On the flip side, -3 has four! They are 1, -3, -1, and 3.
- It’s a whole number
Prime numbers are whole numbers that can’t be divided by any other whole numbers besides 1 and itself.
- It’s greater than 1
The only factor of 1 is 1! That means 1 has only one factor, and prime numbers must have two. Because of this rule, 0 is also not a prime number.
- It’s an odd number
Prime numbers, besides 2, have to be odd. After all, even numbers are divisible by 2, so they’ll always have more factors than itself and the number 1.
List of Prime Numbers up to 100
There are 25 prime numbers up to 100. The prime numbers list up to 100 is as follows: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97.
You can figure out what numbers up to 100 are prime by using the Sieve of Eratosthenes:
- Make a list of numbers 1–100. Cross out 1, since we know that’s not a prime number
- 2 is the first prime number, so circle it
- Next, go through all the numbers and cross out every multiple of 2
- Circle 3. That’s the second prime number
- Now, go through all the numbers and cross out every multiple of 3
- Repeat these steps with every number until they are all either circled or crossed out
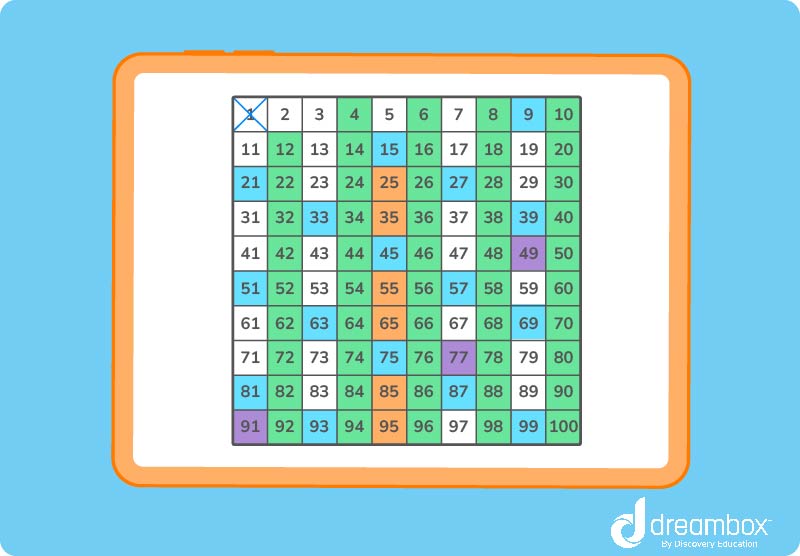
To figure out if a specific number between 1-100 is prime, there is another technique you can try.
If the number is greater than 2 and is even, it’s not prime. If the number ends in a 5, it’s not prime.
Next, determine whether the number is divisible by 3 or 7. If it is, it’s not prime.
Take the number 83 for instance. Is it a prime number?
Well, let’s check!
Is it even? No
Does it end in 5? No
Is it divisible by 3? (8+3=11. 11 is not divisible by 3, so 83 is not either) No
Is it divisible by 7? No
So, 83 is a prime number!
If you answer YES to any of these questions, the number is composite.
Now what about numbers above 100?
There isn’t a strict pattern that prime numbers follow, meaning there isn’t one technique or formula you can use to find all prime numbers.
However, if you’re interested in finding prime numbers between 101-200, just determine whether a number is divisible by 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 and 13. If the number is not divisible by any, it’s prime!
Table of contents
Practice more prime numbers with DreamBox Math!

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Prime and Composite Numbers
Prime and composite numbers make up all positive integers.
All whole numbers besides 0 and 1 are either prime or composite. Since a prime number is a whole number with only two factors, composite numbers are whole numbers with 3 or more factors.
8 is a composite number because it is divisible by 1, 8, 2, and 4.
7 is a prime number because it is only divisible by 1 and 7.
Keep in mind that negative numbers are neither prime nor composite!
FAQs About Prime Numbers
A prime number is any positive number greater than 1 that is divisible only by 1 and itself.
For finding prime numbers up to 100, use the Sieve of Eratosthenes. You can also ask yourself four questions: is the number even? Does it end in 5? Is it divisible by 3? Is it divisible by 7? If you can answer NO to each question, the number is prime. For numbers between 101 and 200, ask yourself whether the number is divisible by 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 and 13. If it is not, it’s prime.
The number 1 only has one factor, 1. That means it does not count as a prime number or a composite number.
The number 2 is a prime number because it can only be divided by 1 and itself.
The prime numbers up to 100 are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


