What is an Integer?
The rules and properties of integers and how to use them

Author
Tess Loucka
Published:
Oct 2024
Key takeaways
- • Integers are a set of numbers that include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero. Fractions and decimals are not considered integers.
- • The sign put before an integer, positive or negative, affects the result of the problem that the integer is a part of.
- • There are 7 properties of integers that are always true and can be used to simplify problems.
You might not realize it, but you use integers every single day! When you’re counting up your allowance, checking how many more pages are left in a chapter you’re reading, or even seeing how far you have to scroll through the TV channels to get to the program you want to watch, you’re using integers.
To put it simply, an integer is a whole number. In school, you work with whole numbers all the time. But what makes integers a little more complicated is that they can also be negative numbers.
There are many rules and properties to remember when working with integers, but first, what is an integer?
Integer Definition
An integer is any positive or negative round number, including zero. A number with a fraction or decimal cannot be an integer, because it is not a round number. After all, the word ‘integer’ literally means ‘whole’ in Latin, so the integer definition makes sense.
Types of Integers
- Zero: Zero is a whole number that marks the point between positive numbers and negative numbers. It is not positive or negative on its own.
- Positive Integers: Positive integers are any whole number greater than zero.
- Negative Integers: Negative integers are any round number less than zero.
Table of contents
Get more math practice with DreamBox!
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Integers on a Number Line
To visualize integers, place them on a number line. A number line is a horizontal line that goes on for infinity on both sides. Numbers are placed on the line in relation to each other using equally distanced lines and spaces.
When setting up a number line, 0 is placed in the middle. As numbers get bigger, they move to the right. Smaller numbers go to the left.
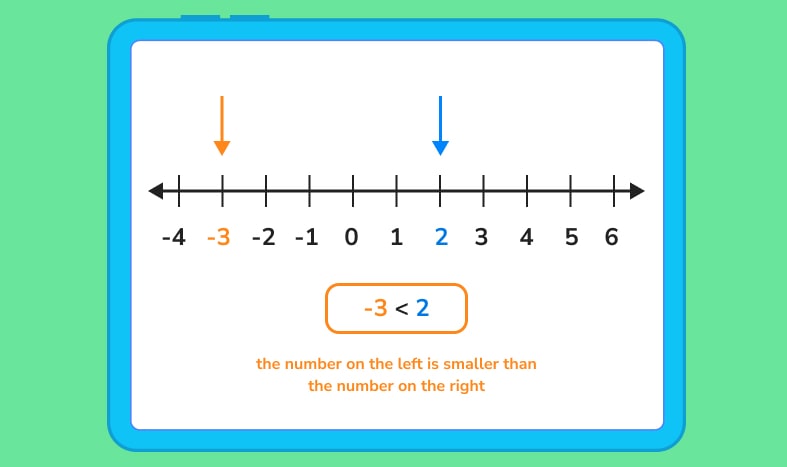
When placing integers on a number line, you often start off with an integer set. Integer sets are lists of integers notated as Z = {list of integers}
Here’s an example integer set: Z = {-5, -2, 1, 3, 6}
As you get into more advanced integer graphing, you may come across the term greatest integer function. The greatest integer function is denoted as [x] = y. In this function, y is the largest integer that is less than or equal to x. Think of it as rounding down.
For example, [3.4] = 3 because 3 is the largest integer less than or equal to 3.4
[-3.4] = -4 because -4 is the greatest integer less than or equal to -3.4 (remember to move left on the number line!)
Integer Operations
So, what is an integer operation and how do you use integers in math problems?
Integer operations are basic operations that can be done using integers. To complete these operations, you’ll need to use the integers’ absolute values. The absolute value of an integer is the number value, or the distance away from zero. As a result, absolute value will always be positive.
So, 2 would be the absolute value of both |2| and |-2|. The absolute value of both |-43| and |43| is 43.
Adding and Subtracting Integers
Adding integers of the same sign (positive or negative) will always result in an integer with that same sign.
(+3) + (+8) = +11
(-3) + (-8) = -11
Adding integers with different signs will result in an integer with the same sign as the number with the larger absolute value. To solve these problems, subtract the integers’ absolute values and use the sign of the number with the larger absolute value.
(+3) + (-8) becomes |8| – |3|, which is 5. The 8 is larger than the 3, and it is negative, so 5 becomes -5.
(-3) + (+8) also becomes |8| – |3|, which is 5. The 8 is larger, but it is positive, so 5 becomes +5.
When subtracting integers, change the sign of the second number and add the numbers together.
(+3) – (+8) becomes (+3) + (-8) = -5
(-3) – (-8) becomes (-3) + (+8) = 5
Multiplying Integers
When multiplying integers, the result will be positive if both integers have the same sign. That’s true whether the sign is positive or negative. The result will be negative if both integers have different signs.
(+3) x (+8) = +24
(+3) x (-8) = -24
Dividing Integers
The rules for dividing integers are the same as they are for multiplying them. If both integers have the same sign, the result is positive. If both integers have different signs, the result is negative.
(+10) ÷ (+5) = +2
(+10) ÷ (-5) = -2
If there are not enough integers examples throughout this article for you, you can find countless more integer practice problems and help with online resources. Math apps and websites can provide you with more definitions, examples, and practice problems until you feel confident with this topic.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Properties of Integers
Closure Property
According to this property, when you add, subtract, or multiply two integers together, the result will always be an integer. Dividing any two integers does NOT always result in an integer.
Ex. 8 + 4 = 12
8 – 4 = 4
8 x 4 = 32
8 / 4 = 2, but 4 / 8 = ½ or .5 (fractions and decimals are not integers)
Associative Property
According to this property, rearranging the grouping of integers does not change the result when performing addition or multiplication.
In other words, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
Similarly, a x (b x c) = (a x b) x c
The placement of the parentheses doesn’t matter. The answer will always be the same. However, this is not true for subtraction or division.
Commutative Property
Similar to the Associative Property, this property states that the order of integers in an addition or multiplication problem does not affect the result.
So, a + b = b + a and a x b = b x a
Additive Property
This property states that adding two of the same integers together with different signs always results in 0.
Ex. 2 + (-2) = 0. In this case, -2 is the additive inverse of 2.
(-2) + 2 = 0. In this case, 2 is the additive inverse of -2.
An additive inverse is any integer that, when added to another integer, results in 0.
Distributive Property
This property states that when using the form a (b + c), the integer in place of “a” can be distributed to “b” and “c” to become (a x b) + (a x c).
Ex. 3 (2 + 8) = (3 x 2) + (3 x 8) = (6)(24) = 30
Multiplicative Inverse Property
This property states that any given number multiplied by itself over 1 is equal to 1. This is written as a + a/1 = 1.
Ex. 5 x 5/1 = 1
Identity Property
This property states that any integer plus 0 is equal to the integer itself, while any integer multiplied by 1 is equal to the integer itself.
Ex. 8 + 0 = 8
8 x 1 = 8
Integer Practice Problems
Click on the boxes below to see the answers!
Answer: +12
When subtracting two integers, change the sign of the second integer, and add the integers together. (+9) – (-3) becomes (+9) + (+3), which is equal to +12 or 12.
Answer: +4
When dividing two integers with the same sign, the result will always be positive. Three goes into 12 four times, so the answer is +4 or 4.
Answer: +1
Solve what is within the parentheses first. Multiplying two integers with different signs results in a negative number. So, (+2) x (-3) equals -6. Now, add +7 to -6 to get +1 or 1.
FAQs about integer numbers
Integers are any positive or negative numbers, including zero. Integers are not fractions or decimals.
Yes, zero is an integer.
Consecutive integers are integers that follow each other in order from smallest to largest by 1.
Positive integers and 0 are whole numbers. Negative integers are not.
Yes, all integers are rational numbers because when turned into fractions, they have a denominator of 1.
Decimals are not integers. Integers must be round numbers.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.
