Master Measurement
Dive into articles that turn math struggles into successes with engaging content crafted to boost kids’ math skills.
Measurement exists in practically everything we do, from planning our daily schedule to baking a cake! In today’s world, we understand so many things through units of measurement. That’s why understanding the different forms and common units of measurement is such a crucial skill. Let’s learn about the different ways measurement can be used to understand the world around us!
Browse Most Popular Articles:
Time is told using the numbers on a digital clock or the hands on an analog clock using hours, minutes, and seconds. Learning to read a clock is crucial to staying on track in your daily life!
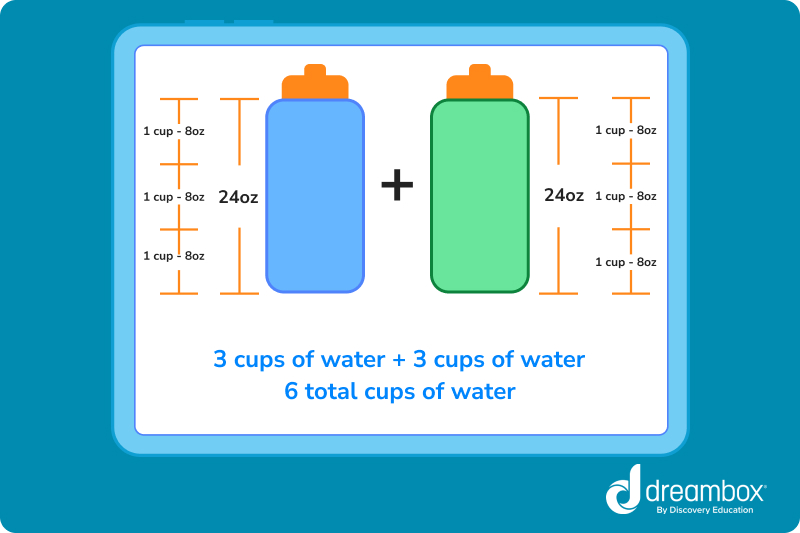
Learn how to convert popular unit units of measurement like hours to minutes, feet to miles, or pounds to ounces.
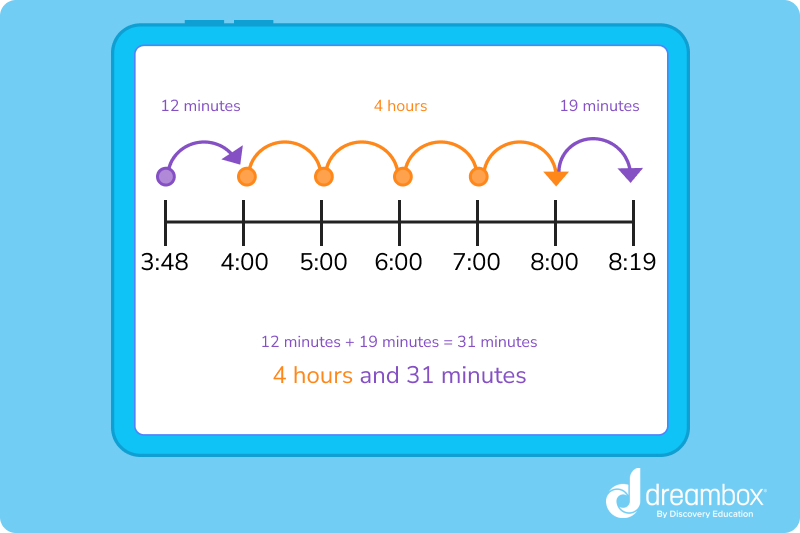
Learn how to calculate the time between the start and end time of an event, known as elapsed time.
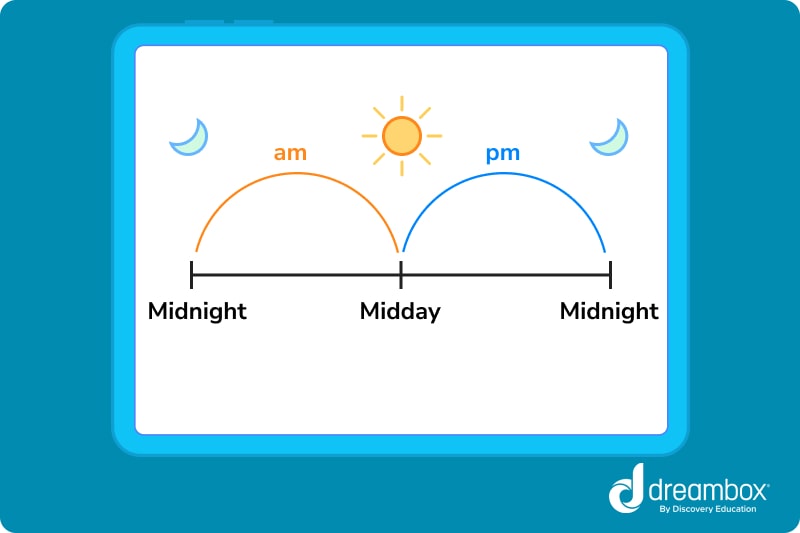
Learn the difference between AM and PM— labels we use to distinguish between the first half and second half of the day.
Browse All Measurement Skills:
Measuring flour for a cake. Taking the temperature outside. Reading a ruler to calculate the length of a picture frame. We use units of measurement every single day! Understanding this crucial math skill begins by learning the metric and customary systems of measurement. Dive into any resource below to learn more.
A system of measurement that centers around grams, liters, and meters to measure weight, volume, and distance respectively. This is a decimal system and focuses on 10 and multiples of 10. It is commonly used around the world.
A system of measurement commonly used in the United States and US territories that uses customary units to make day-to-day measurements. It is based on the imperial and English units used in the 13 colonies.
Mass is the measurement of how much matter makes up a given object. Mass is often measured using a scale or graduated cylinder. Units used to measure mass include grams, kilograms, ounces, pounds, and tons.
Temperature is the measurement of how hot or cold something is. It is measured using a tool called a thermometer. Common units of measurement are Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin.
Capacity is the measurement of how much an object can hold or contain before spilling over. You can use a graduated cylinder for this. Common units include milliliters, liters, fluid ounces, quarts, and gallons.
Rulers measure the length of an object or the distance between two points. Rulers, yard sticks and straight edges are labeled with units of measurement such as millimeters, centimeters, inches, and feet.
Unit conversion is changing a measurement from one unit to another while ensuring both numbers are equivalent. Common unit conversions include hours to minutes, feet to miles, or pounds to ounces.
Time is told using the numbers on a digital clock or the hands on an analog clock using hours, minutes, and seconds. Learning to read a clock is crucial to staying on track in your daily life!
Elapsed time is the time that exists between two specific points in time. It is determined using the start and end time of an event and is explained in terms of seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, and years.
Time conversion involves taking a length of time and labeling it according to different yet equivalent time units. Common time unit conversions include changing minutes to hours, days to weeks, or minutes to seconds.
All About Measurement
A simple measurement definition is a characteristic of an object or event determined by comparing it to known quantities. When you measure something, you are comparing it to standardized units and discovering how it can be correctly labeled according to a system of measurement.
Before there was any standardized unit of measurement, people used all sorts of things to make measurements!
Ancient Egyptians and Babylonians used lengths of forearms, hands, and fingers to determine length. For much of human history, humans used sun and moon movements and constellations to determine time.
Irish farmers used their own unit, the “cow’s grass,” to measure the size of their fields. One cow’s grass was the size of land that could produce enough grass to support one cow.
You can imagine how disorganized those systems of measurement probably were! Today, we have three main standardized systems of measurement. Let’s take a look at them.
What Are The Systems of Measurement?
Metric Units of Measurement
The metric system is a decimalized system developed in France in the 1790s. It uses the number 10 and its multiples.
The metric system was used to develop the SI (International System) units of measurement, an official system of units used to standardize science and commerce. SI base units borrow from the metric system but are not totally the same.
- The base SI units of measurement list is the second (time), meter (length), kilogram (mass), ampere (electric current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity).
- Metric units of length include the kilometer, hectometer, dekameter, meter, decimeter, centimeter, and millimeter.
- Metric units of weight include the kilogram, hectogram, dekagram, gram, decigram, centigram, and milligram.
- Metric units of volume include the kiloliter, hectoliter, dekaliter, liter, deciliter, centiliter, and milliliter.
Standard Units of Measurement
The standard system of measurement in the US is also referred to as the customary system. The precursor of this system is the English system used by the Anglo-Saxons and Romans over a thousand years ago!
This medieval English system of measurement was officially turned into the imperial system in the UK in 1826. In the US, the English system became the customary system and officially became the standardized measurement system for the United States in 1832.
- Customary units of length include the miles, yard, foot, and inch.
- Customary units of weight include the ounce, pound, and ton.
- Customary units of capacity include the fluid ounce, pint, cup, quart, and gallon.
Imperial Units of Measurement
The imperial system became the official system of measurement in the UK in 1826. It used many of the same units as the customary system, such as the foot, yard, mile, acre, fluid ounce, pint, quart, and gallon.
However, while the names of the units are the same, the measurements of the units have minor differences.
The imperial system was used throughout the UK for over a hundred years until it was replaced with the metric system in the mid-1900s.
Measurement in Everyday Life
We make measurements all the time, whether we realize it or not. When we figure out how early we have to wake up in the morning according to what time we have to be at school that day, we’re thinking about time measurement.
When we go clothing shopping, our size is another standardized system of measurement that we use to find clothes that fit.
Measurement is all around us, which is why having a firm grasp of the topic is so important!
FAQs About Units of Measurement
Measurement is the comparison of an object or event with a known system of units to determine a specific characteristic about it.
Students as young as 5 may begin learning about measurement. Children can make non-standardized comparison measurements from an even younger age, but comprehension of standard units and numbers comes around 1st grade.
SI units of measurement are the international system of units used in science and commerce around the world. The SI base units are the second, meter, kilogram, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela.
As your child advances to different grade levels, their understanding of Geometry math concepts is broadened. Fifth-grade math has the highest level of geometry math concepts of the grades in elementary. If your child stays on track, these more challenging concepts can easily be learned and practiced.
The three common systems of measurement are the metric system, the customary system, and the SI system.
Grades
If you’ve ever wondered how to help your child with math homework or what they should know by the end of fifth grade, these elementary math resources are for you.
Choose a grade level below to browse math skills and objectives by grade.
It’s time to build on what we’ve learnt so far and develop mathematical fluency.
Level up number knowledge with the introduction of multiplication, division and fractions.
Classifying, analysing and problem-solving: we’re applying all our skills here!
Understanding is extended even further across number, measurement and geometry.
Meet ratio, rational numbers and equations – this is where we explore statistical thinking.
Children learn more advanced topics like pre-algebra and investigate complex statistics and probability.
Introduce problems involving shape, scale drawings, population samples and more.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.