What Are the Divisor and the Dividend?
Let’s split up these elements of division and break down exactly what they are.

Author
Jill Padfield
Published:
Oct 2024
Key takeaways
- They are the two main parts of any division problem – Simply put, the dividend is the number getting divided, and the divisor is what we are dividing that number by.
- Together, divisor and dividend will get you your quotient – The quotient is the answer to your division problem, the exact number of times you can divide one number by another.
- Stay alert for some special situations – While divisor and dividend are basic enough concepts, there are a few circumstances that might complicate matters.
As with any math problem, understanding the mechanics behind the numbers demands an understanding of exactly what is happening. Math isn’t just magic after all, even if it may seem that way sometimes. To talk about those seemingly mysterious mechanics, you need to know a few terms so you can wrap your head around the ins and outs of the explanations.
With division, you need to understand the two core components of any division problem, the divisor and the dividend. With those concepts bouncing around in your head, you’ll soon be able to unlock the power of division.
What’s the dividend?
Let’s say you are a very generous person and have a dozen fresh donuts you want to share among yourself and your three friends. What we have here is a simple division problem of 12 ÷ 4, the 12 being the number of donuts you have to share and 4 being the number of people about to chow down on said donuts (yourself included, of course). 12 is the number being divided, so that makes it the dividend.
Any number that is being divided up one way or another is the dividend. It doesn’t matter how big or small, that number will always be the dividend.
You may also see the word “dividend” pop up in other places, too. For example, when companies are looking to divide up profits among people who invested, they call those portions of profits dividends, too. This can be a little confusing since “dividend” as we will use it speaks to the number being divided, while the business world dividend is a portion. Just keep that in mind if you see “dividend” out in the wild. The meaning changes depending on where you see it.
What is the divisor in math?
If the dividend is the number being divided, naturally, the divisor is the number of times the dividend is getting divided.
Let’s return to your wholesome donut distribution from earlier. 12 was the number of donuts you had to share, and you wanted to split those donuts among yourself and 3 friends. We would write that problem out like 12 ÷ 4. As we discussed earlier, the 12 is the dividend, so that makes the 4 the divisor.
One way to look at division is as the reverse of multiplication. In multiplication, you are grouping a bunch of sets of numbers together, and in division, you are breaking them back up.
Table of contents
Access more math practice with DreamBox
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

How do you spot the divisor and dividend?
Division problems can take many different forms, and the location of the divisor and the dividend can change depending on the format. Here’s where to look for each type of division problem.
First, the basic format of a division problem looks like 12 ÷ 2. You read this like 12 divided by 2, so that means that 12 is the number getting divided up, making it the dividend. We’re dividing by 2, so that makes 2 the divisor.
Another format you might see is a simplified version that uses a line to indicate division. First, you’ll see problems like 12/2, with a little slash mark replacing the division sign. Here, you read the problem just like normal. 12 divided by 2. The number on the left will always be the dividend, and the number on the right is the divisor.
The second way you can see a line replace the division symbol is with something like this:
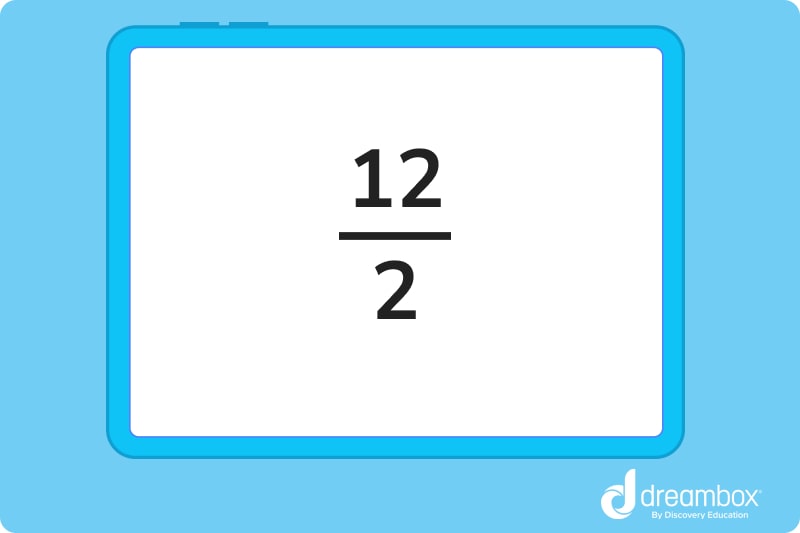
Where you normally read division problems from left to right, here you read from top to bottom. 12 divided by 2. The top number is our dividend and the bottom is the divisor.
The last way you are likely to see divisor and dividend is in long division format. That looks like this 2⟌12, with one of the numbers in a little house-looking symbol. This one is a little different than the others because the dividend is actually the number on the right this time, the one in the little house. You would read this problem like 12 divided by 2, making the 12 the dividend again. This format exists for longer, more complicated division problems, which is why the order of the numbers is different.
Additional tips for divisors and dividends
As usual, there are a few special rules to remember when looking at divisor and dividend. For one, the dividend doesn’t always have to be bigger than the divisor. Back to the donuts from before, what if you weren’t so lucky as to have a full dozen to share? What if you had just 1 donut for all of your friends? You still want to share, so you would be dividing 1 by 4. When the dividend is smaller than the divisor, your answer (the quotient) will be a decimal or a fraction.
Getting the fraction is easy enough, since that will just be an expression of how you are dividing up the dividend. Your donut situation would get you a 1⁄4, one being the donut, and 4 being you and your friends. The decimal value of 1⁄4 is .25, but you can learn more about that in another lesson.
Another thing to remember is that if your divisor is 1, the answer will always be the dividend. If you wanted to eat that dozen of donuts all by yourself, you would be dividing 12 by 1, which is just 12 since you, the 1, will get all 12 donuts.
The inverse of this is true, too. If you divide a dividend by a divisor of the same value, 12 ÷ 12, for example, the quotient will always be 1.
The last thing to note is that a divisor can never be 0. Think about it, if you have those twelve donuts and want to give them to no one, including yourself, what would that even look like? This is why if you plug any problem with a divisor of 0 into a calculator, you will get an answer of “undefined.” Mathematicians are still trying to find ways to divide by 0, but for now, that mystery remains unsolved. Maybe you will be the one to crack it one day!

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Let’s practice together!
1. Which number is the divisor in the following problem?

Here the divisor is 10 since we are trying to split 32 up into 10 smaller groups.
2. Which number is the dividend in the following problem?

Here the dividend is 120 since this is the number we are trying to divide by 12.
3. Which number is the dividend in the following problem?

Here the number in the little house is the number being divided up, which means 35 is the dividend.
Ready to give it a go?
- See if you can get through all 5 questions on your own. Feel free to look back at the lesson if you get stuck or just need a little reminder.
Practice Problems
Click to reveal the answer.
The divisor is 5, and the dividend is 45.

The divisor is 9, and the dividend is 90.

The divisor is 8, and the dividend is 72.

This is a trick question. The dividend is 57, but this problem has the divisor as 0. Technically, you cannot divide by 0, so this problem could not be solved.

The missing divisor is 1.

Parent Guide
-
1. The divisor is 5, and the dividend is 45. How did we get here?
- 1. Dividend is the number getting divided, so that would be 45
2. Divisor is how many groups we divide into, so that would be 5 -
2. The divisor is 9, and the dividend is 90. How did we get here?
- 1. Dividend is the number getting divided, so that would be 90
2. Divisor is how many groups we divide into, so that would be 9 -
3. The divisor is 8, and the dividend is 72. How did we get here?
- 1. Dividend is the number getting divided, so that would be 72
2. Divisor is how many groups we divide into, so that would be 8 - 4. This is a trick question. The dividend is 57, but this problem has the divisor as 0. Technically, you cannot divide by 0, so this problem could not be solved.
-
5. The missing divisor is 1. How did we get here?
- The quotient is 67 and the dividend is 67. The only way these two could be the same number is if the divisor is 1.
FAQs about the divisors and dividends
The dividend is the number being divided up, and the divisor is the number of groups you divide the dividend into.
You are not able to divide any number by 0, so the divisor cannot be 0.
The dividend will either be the number on the left of standard division expressions or on the top when division is expressed like a fraction. For long division expressions, the dividend is one the right.
If you are trying to divide a number by a larger number, your answer, the quotient, will either be a decimal or a fraction. If you are trying to write out a decimal as your answer, remember to put a zero in front of the decimal as a reminder that your answer cannot be 1 or greater.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


About the Author
Jill Padfield
Jill Padfield has 7 years of experience teaching mathematics, ranging from Algebra 1 to Calculus. She is currently working as a Business Analyst, working to improve services for Veterans, while earning a masters degree in business administration.