Cones
Cones are 3-D shapes that exist all around us. Understanding the cone shape helps build a strong mathematical foundation.

Author
Tess Loucka
Published:
March 2025
Key takeaways
- • There are two types of cones - right circular and oblique.
- • The total surface area of a cone is the area of both the base and lateral surface and can be found using the formula πr(l + r).
- • The volume of a cone is found with the formula ⅓πhr^2.
Cones exist all around us. Not only are cones an important part of geometry but they are also used in science, medicine, construction, design, and visual art. Once you understand the basics of cone shapes, the vast and complex world of 3-D shapes will be much easier to understand!
Let’s dive in. What exactly is a cone?
What is a cone?
A cone is a 3-D shape that has a flat, circular base and a curved surface that angles toward a single point called a vertex or apex.
The curved surface of the cone is also called the lateral or side surface.
Table of contents
Strengthen your math skills with DreamBox
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Real-life examples of cone shapes
The cone shape has three distinct properties. These are:
- A cone has no edges.
- A cone points toward a single apex.
- A cone has one circular base.
Although all cone shapes have these properties, there can still be variations to the cone shape.
The first common cone shape is the right circular cone.
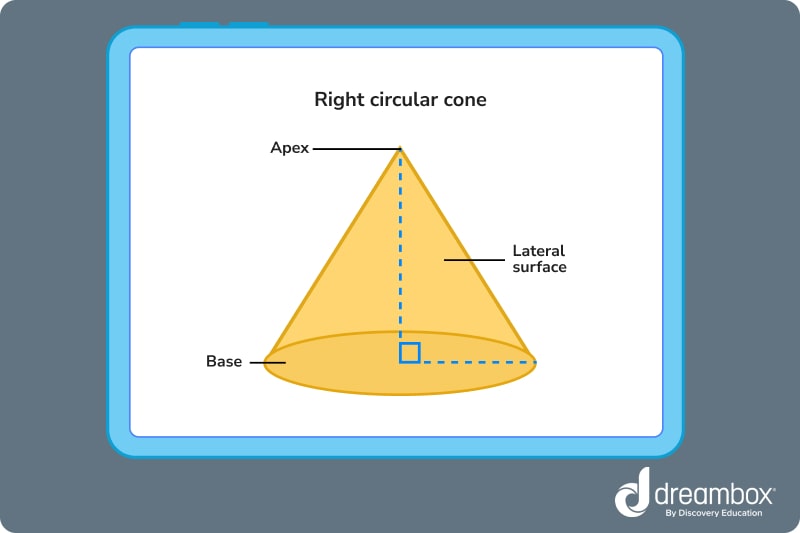
Right circular cones have an apex perpendicular to their base. The right angle created in relation to the base and apex is perfectly centered.
Another common cone shape is the oblique cone.
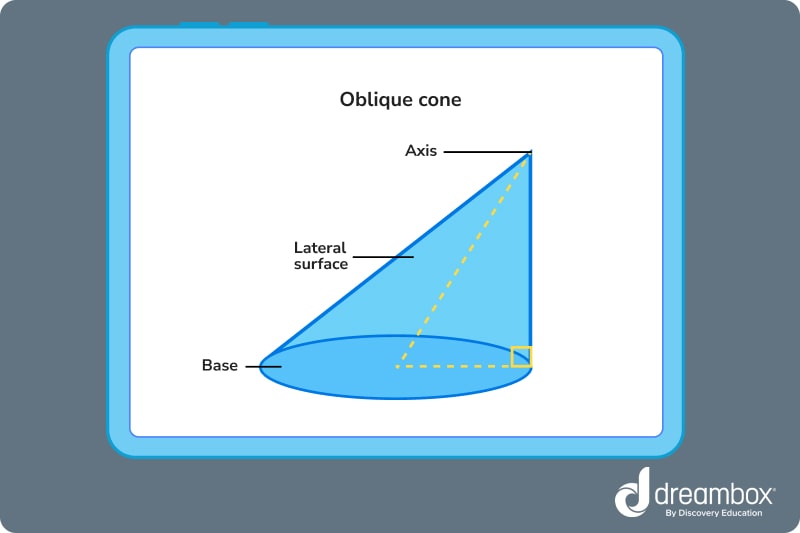
Oblique cones are cones with an apex that is non-perpendicular to the base. If a cone’s apex is at all off-center, the cone is oblique. The right angle created by the apex and base will be off-center as well.
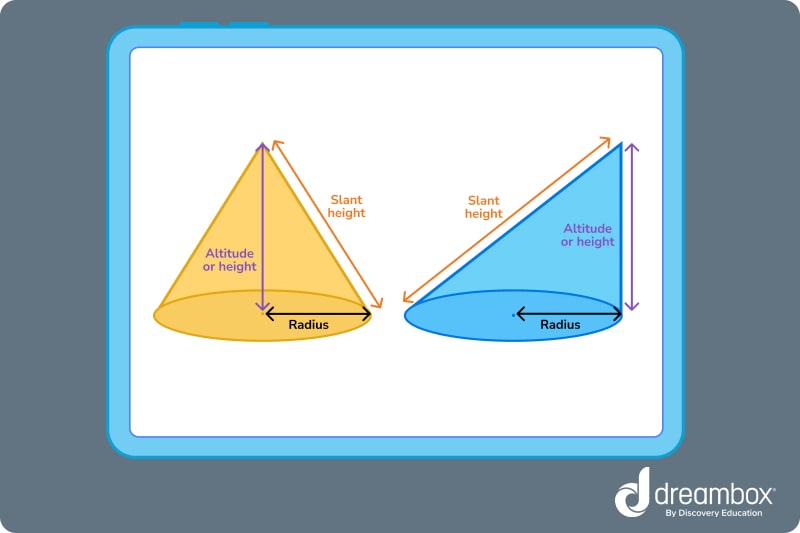
For all cones:
- The radius is the distance from the center of the cone’s base to the cone’s side.
- The slant height is the distance along the side of the cone from the base to the vertex.
- The altitude or height of the cone is the vertical distance from the base to the vertex.
Working with cone shapes
Understanding the way cones work and the formulas used to take their measurements helps students gain a strong foundation in 3-D shapes and geometry.
Finding the volume of a cone
The volume of a 3-D shape is the amount of space the shape contains within its borders.
The formula for finding the volume of a cone is V = ⅓ πhr^2, where r = radius and h = height. Volume is always written in cubic units.
Remember, the radius is the distance from the center of a circle to its side.
This formula takes the area of the circular base, πr^2, and multiples it by the height, h, of the cone, creating the formula πhr^2. This is the same formula for finding the volume of a cylinder.
However, a cone is ⅓ the volume of a cylinder of the same height. Therefore, the formula must be multiplied by ⅓.
Let’s test this formula out with the example below!
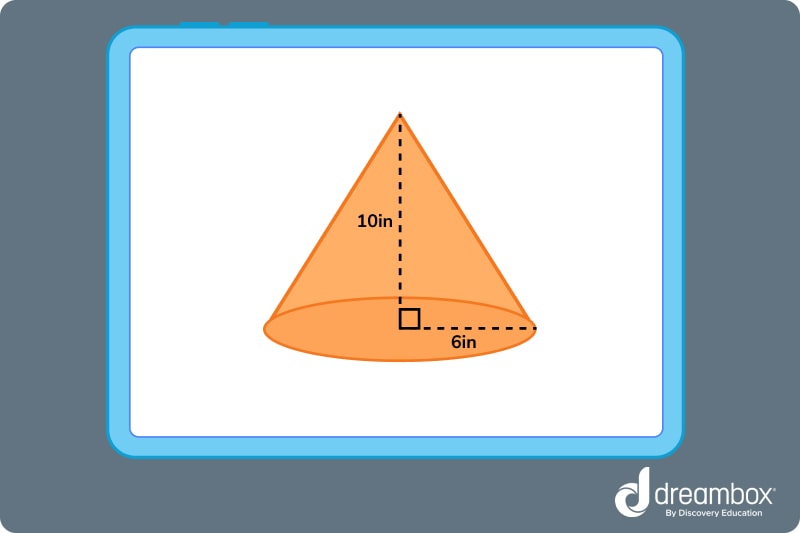
As we can see from the image above, the radius of the cone is 6 inches. This means r = 6.
The height of the cone is 10 inches. So, h = 10.
We can rewrite π as 3.14.
Now, plug those numbers into the formula.
V = ⅓ πhr^2 = ⅓ x 3.14 x 10 x 6^2) = ⅓ x 3.14 x 10 x 6 x 6 = ⅓ x 1130.4 = 376.8
The volume of this cone is 376.8 cubic inches.
Finding the surface area of a cone
The surface area of a 3-D shape is the combined area of every one of its sides. The total surface area of a cone is the combined area of its base and its curved surface.
The formula is Total Surface Area = πr(l + r) where r = radius and l = slant height.
The surface area is written in squared units.
Let’s look at the example below!
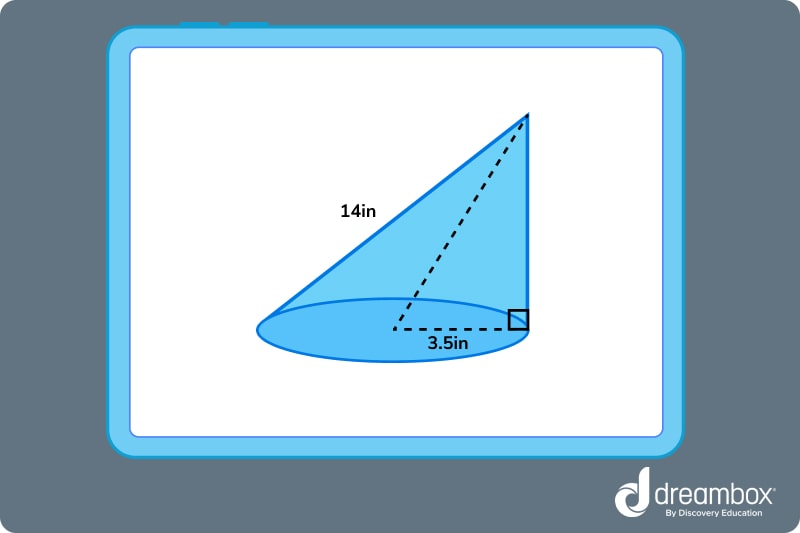
From the image above, we can conclude that r = 3.5 and l = 14.
We can replace π with 3.14.
Now, plug those numbers into the formula:
Total Surface Area = πr(l + r) = 3.14 x 3.5 x (14 + 3.5) = 3.14 x 3.5 x (17.5) = 10.99 x (17.5) = 192.325
The total surface area of the cone is 192.325 inches squared.
To find just the curved surface area, use the formula πrl.
For more practice with identifying and measuring cones, check out a professional math website, or use a workbook. Practice makes perfect and the more you practice, the more confident you’ll feel with 3-D shapes.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Practice problems
Test your knowledge of vertical lines with the practice problems below:
Question 1: Is this cone right circular or oblique? Why?
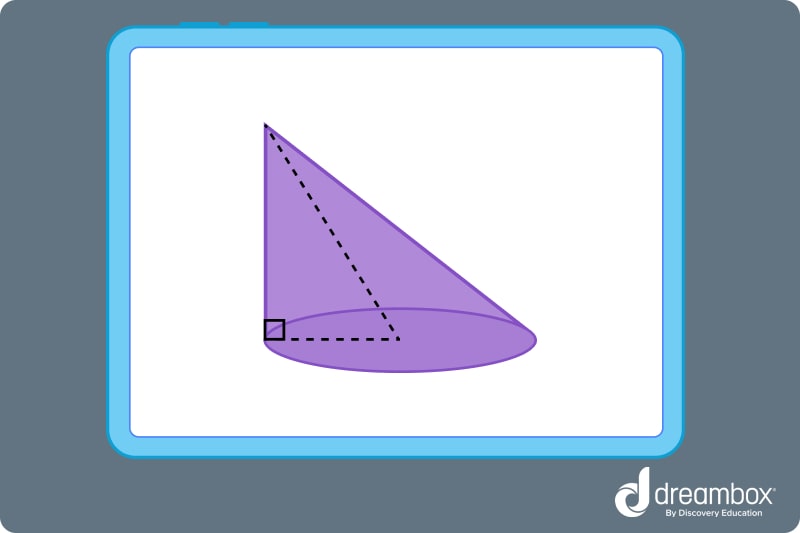
Answer: This cone is oblique because the vertex is not perpendicular to the base.
Question 2: Find the total surface area of the cone.
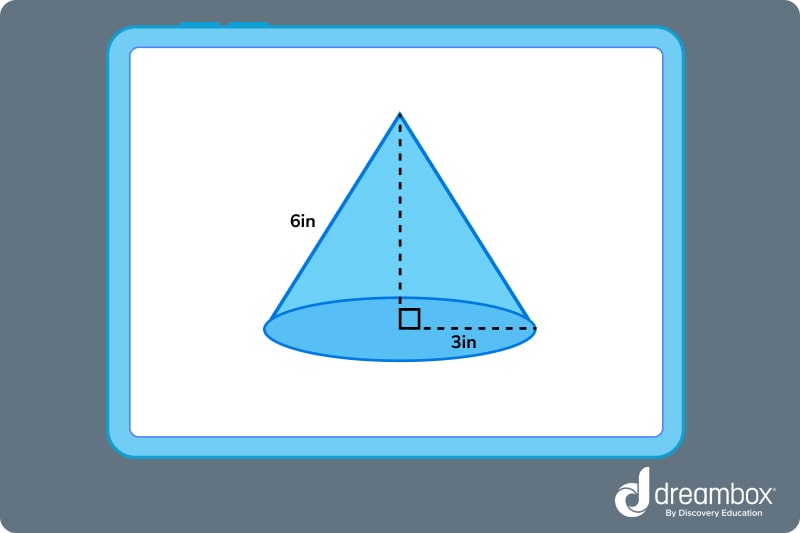
Answer: 84.78 cubic inches.
Question 3: What is the volume of this cone? Round to the nearest tenth.
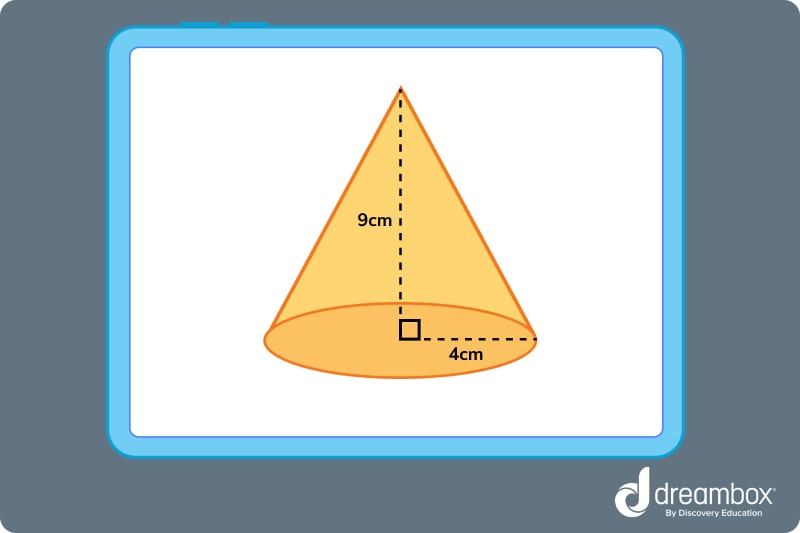
Answer: 150.7 cubic centimeters
Parent guide
Question 1: Oblique cones have a vertex that is not aligned with the center, or perpendicular, to the base. Therefore, this cone is oblique.
Question 2: The formula for the total surface area of a cone is πr(l + r). When we replace r with 3, l with 6, and π with 3.14, we can solve the equation to get 84.78 cubic inches or 84.78 in^3.
Question 3: The formula for the volume of a cone is V = ⅓ πhr^2. Plug 4 in for r, 9 in for h, and 3.14 in for π. Solve the equation to get 150.72, then round to the nearest tenth. The units are centimeters. So, the volume is 150.7 cubic centimeters or 150.7 cm^3.
FAQs about cones
Real-life examples of cones include party hats, traffic cones, ice cream cones, volcanoes, and funnels.
Cones are usually introduced in 1st or 2nd grade, but taking their measurements is often taught in 8th grade.
The volume of a cone can be found with the formula V = ⅓ πhr^2.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


