What are congruent shapes?
The ins and outs of congruency and how to apply the concept to any figure in geometry.

Author
Tess Loucka
Published:
March 2025
Key takeaways
- • Congruency in math means identical. Two congruent shapes perfectly overlap each other.
- • Congruent sides have the same length and position in a shape.
- • Congruent angles have the same angle measurement.
Congruency Definition
In math, the word congruent means the same. Two things that are congruent will perfectly overlap each other when overlaid.
The congruency symbol in math is ≅ and is read as “is congruent to.” For example, <B ≅ <D is read as “angle B is congruent to angle D.”
Think of a window and picture it reflected in a mirror. The window and its mirror image are congruent because they are identical.
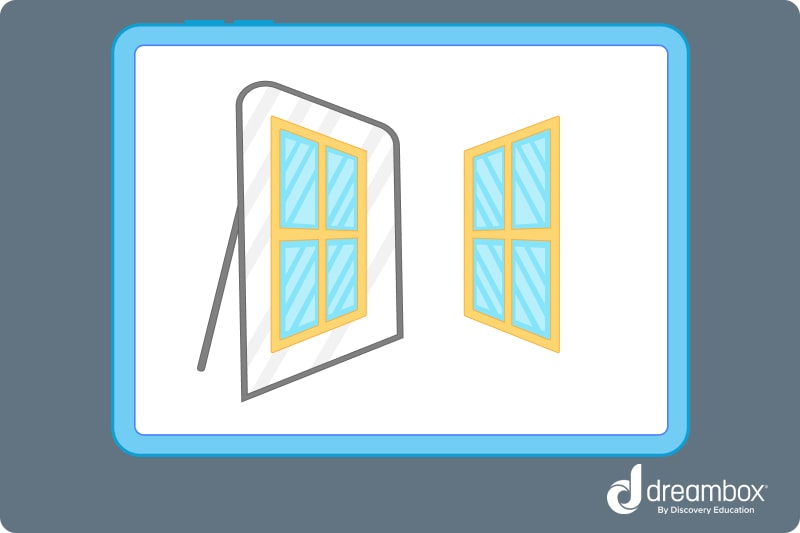
Types of Congruency in Math
Although congruency is always synonymous with sameness or being identical, the way to identify congruency in figures can differ.
Congruency depends on correspondence, so understanding one is essential to understanding the other. In math, correspondence means the same thing as relation. It is the relation between different parts of one or more figures.
The correspondence symbol is ≙ and is read as “corresponds to.”
Look at the two triangles below:
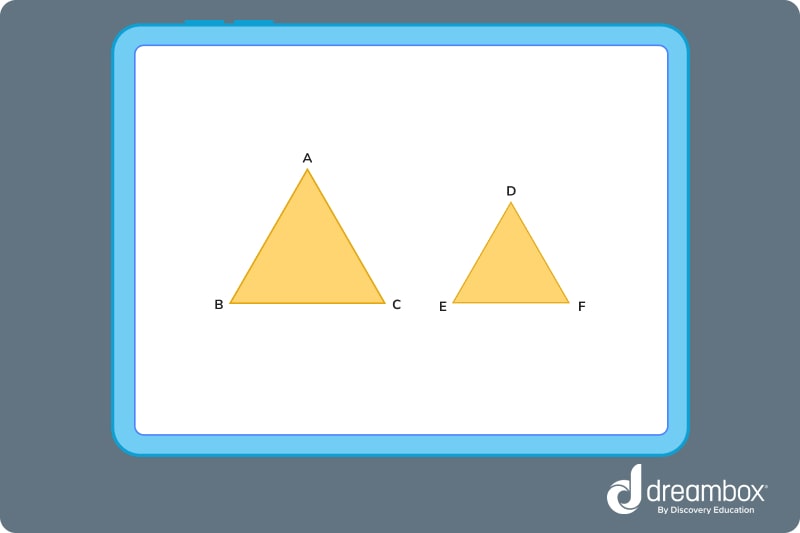
Although these two shapes are clearly different sizes, we can see that many of their characteristics are the same.
We can say that point A ≙ point D because they are in the same position as each other. Following this logic, we can also say that line BC ≙ line EF because, once again, they are in the same position.
For shapes, lines, and angles to be congruent, they must correspond to each other.
Table of contents
Access more math practice with DreamBox
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Congruent Shapes
Congruent shapes are any shapes that are identical to each other. To be congruent shapes, the angles and sides of one shape must correspond to all the angles and sides of the other.
The two shapes must also be the same size.
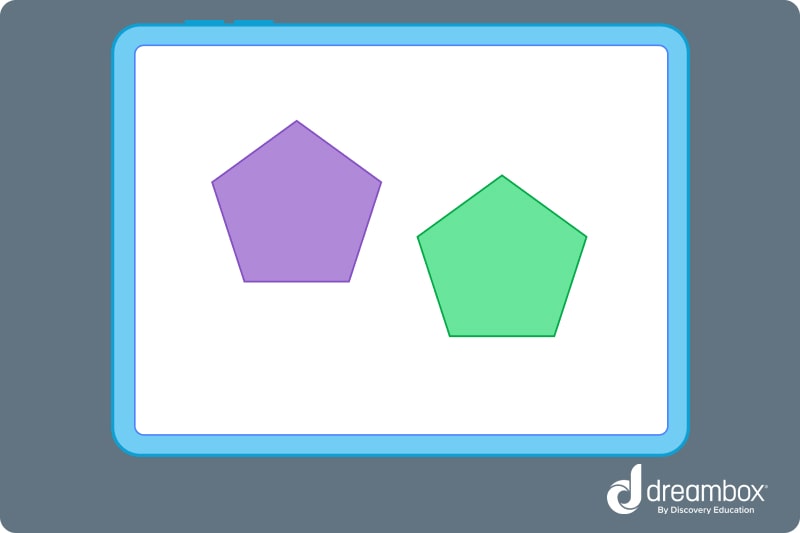
When layered on top of each other, the two shapes above would perfectly overlap.
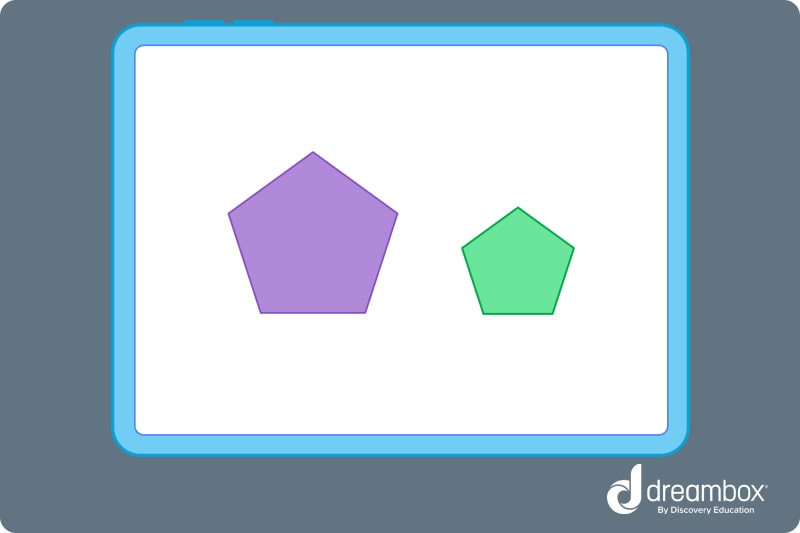
These two shapes have all the same angles, but they are different sizes. These shapes, therefore, are not congruent. However, they do correspond.
For some shapes, there are specific conditions that you can check to determine if they are congruent. These are called Proofs of Congruence.
Two squares are congruent if they have the same area, or all their sides are the same length.
Two quadrilaterals are congruent if their corresponding angles and sides are the same measurements.
For triangles, there are 4 proofs very commonly used in geometry.
Note: Congruent sides are marked with a line. When there are multiple pairs of congruent sides, they are marked with 1, 2, 3, etc. lines. Congruent angles are marked with curved lines.
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS)
Two triangles are congruent if two corresponding sides and the angle they form are the same.
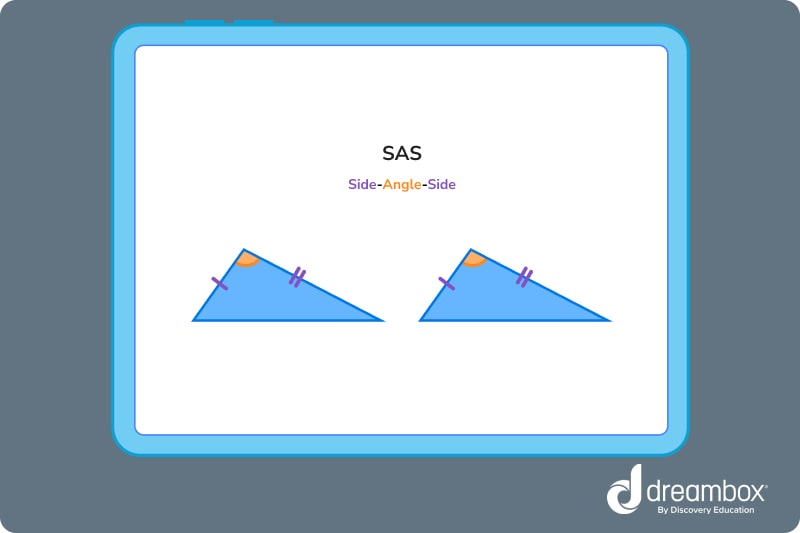
2. Side-Side-Side (SSS)
Two triangles are congruent if all three corresponding sides are the same.
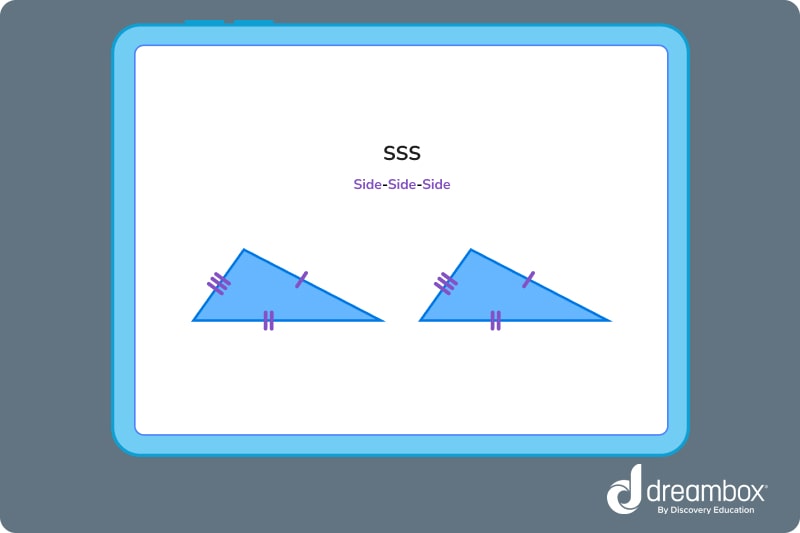
3. Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) or Angle-Angle-Side (AAS)
Two triangles are congruent if two corresponding angles and one corresponding side are the same. The order does not matter.
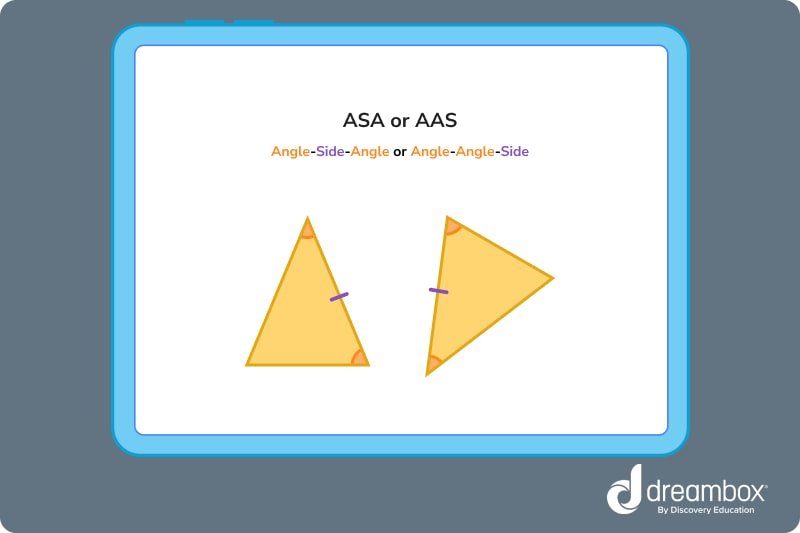
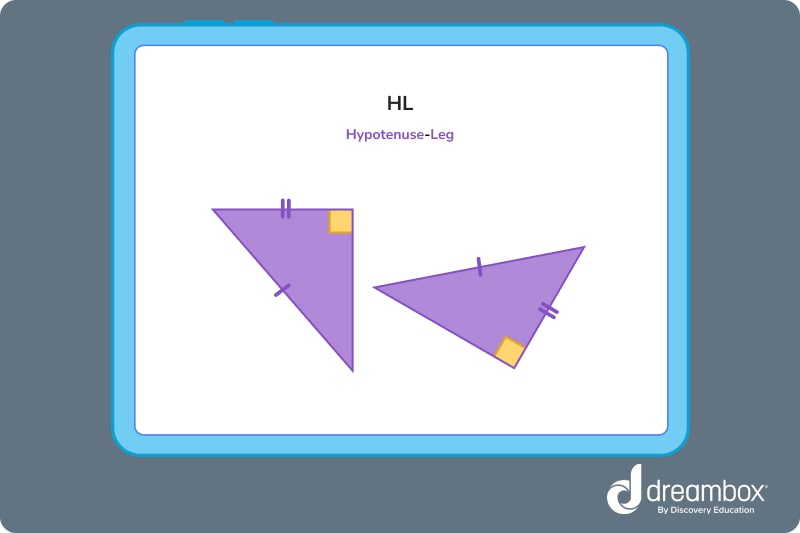
4. Hypotenuse-Leg (HL)
Two right triangles are congruent if their hypotenuse and one other corresponding side are the same. Remember, this is only for triangles that have one 90° angle!

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Congruent sides
So, what is a congruent side?
Two sides said to be congruent have the same length and position in a shape. Congruent sides can exist between multiple shapes or within the same shape.
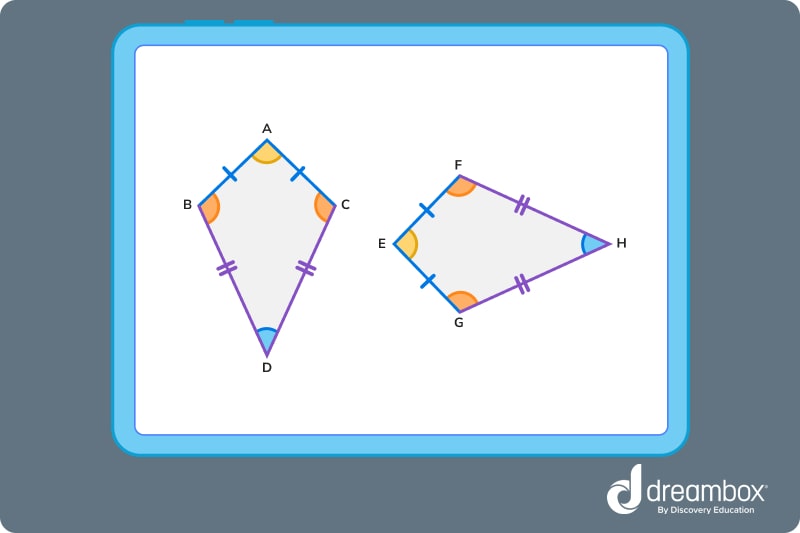
In the quadrilaterals above, sides BD and CD are congruent – they are the mirror image of each other. In the same way, sides AB and AC are congruent.
Sides BD and GH are also congruent. These lines exist on different quadrilaterals but in the same position. They are the same length and, when layered on top of each other, they would overlap perfectly.
We can also see that
Side CD ≅ side FH
Side AB ≅ side EG
Side AC ≅ side EF
Side EG ≅ side EF
Side GH ≅ side FH
When labeling congruent sides, be sure to write the letters in the corresponding order! We wouldn’t say side GH ≅ side HF.
Congruent angles
Congruent angles have the same angle measure. For example, two right angles are automatically congruent because they both measure 90°.
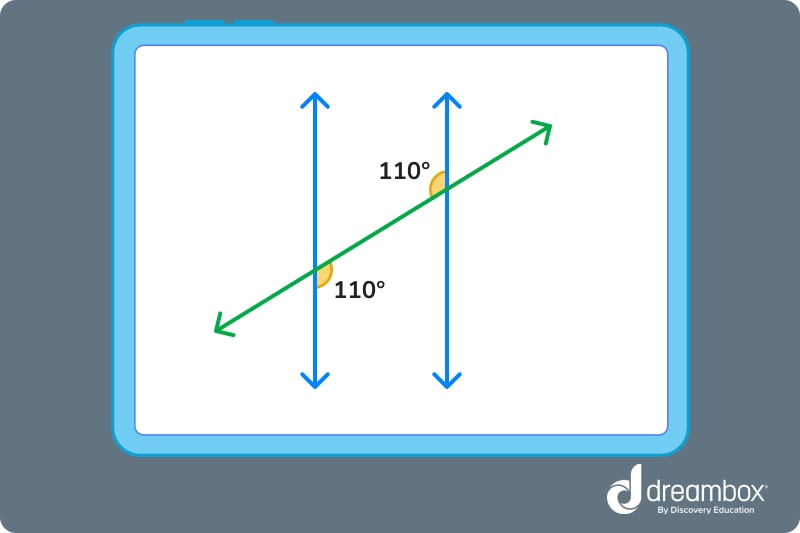
The two labeled angles above measure 110° and are therefore congruent.
Look at the figure below. Can you name all the congruent angles?
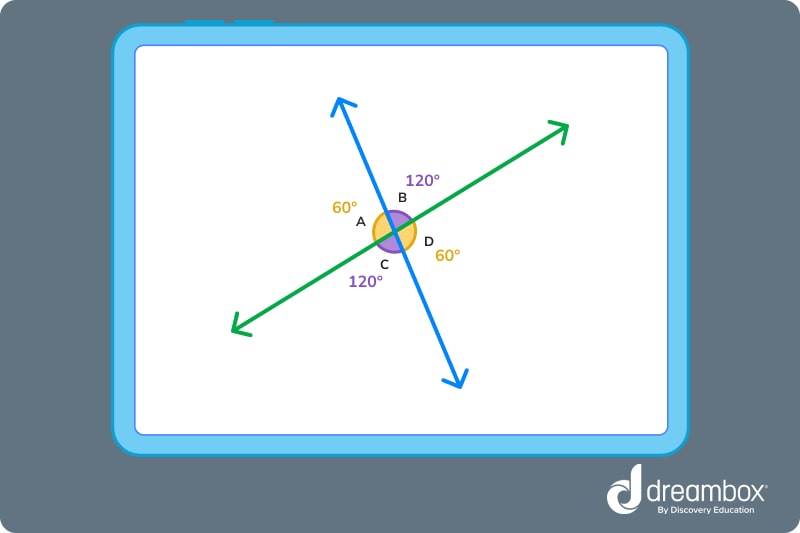
<A ≅ <D. They both measure 60°.
<B ≅ <C. They both measure 120°.
How to recognize congruency
You can determine if shapes, lines, or angles are congruent in multiple ways. The most basic way is to look at them and see whether they are the same size. As we went over before, shapes, lines, and angles that can overlap perfectly are congruent.
Whether they are facing the same direction or are mirror images of each other, if they are the same size, they are congruent.
Other ways to recognize congruency is by using congruency theorems like the ones above: SAS, SSS, ASA, AAS, and HL.
When dealing with squares, rectangles, or other polygons, you can determine whether they are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are congruent.
To learn more about the role congruency plays in geometry, you can take lessons, complete practice questions, and read through detailed explanations using professional math apps, web apps for math help, or workbooks.
<A ≅ <D. They both measure 60°.
<B ≅ <C. They both measure 120°.
Congruent Shapes Practice Problems
Q.1
Quiz Complete!
You got 0 out of 0 questions correct.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


About the Author
Tess Loucka
Tess Loucka discovered her passion for writing in high school and has not stopped writing since. Combined with her love of numbers, she became a math and English tutor, focusing on middle- and high-school-level topics. Since graduating from Hunter College, her goal has been to use her writing to spread knowledge and the joy of learning to readers of all ages.