What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
Thousands of years ago, a Greek philosopher named Pythagoras discovered a formula to help us solve the lengths of a right triangle. It’s called the Pythagorean theorem — let’s learn more!
Author
Lucy Hart
Published:
Dec 2024
Key takeaways
- • The Pythagorean theorem formula is a² + b² = c².
- • It only works for right triangles.
- • To solve the Pythagorean theorem, we need to know the lengths of at least two sides of a right triangle.
- • The Pythagorean theorem formula can be used to find the length of the shorter sides of a right triangle or the longest side, called the hypotenuse.
Over 2,000 years ago, a Greek philosopher called Pythagoras created a very famous theorem about triangles. It lets you work out the length of any side in a right-angled triangle!
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem states:
“In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides.”
This may sound a bit complicated, but it makes a lot more sense when we look at what it’s saying in the form of a picture:
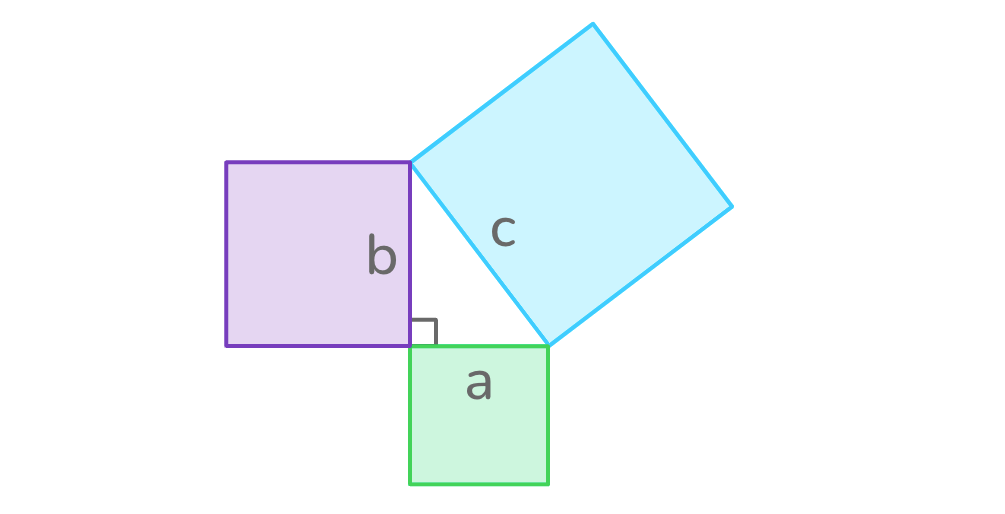
When squares are drawn along each side in a right triangle, the total area of the two smaller squares (those along the shortest sides, a and b) is the same as the area of the largest square (the square along the longest side, c).
By working out the area of each square, we can find the length of any side in a right triangle. And luckily, Pythagoras created a handy formula to help us do this!
Table of contents
Get math practice with DreamBox!
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Pythagorean theorem formula
The formula for Pythagoras’ theorem is a² + b² = c².
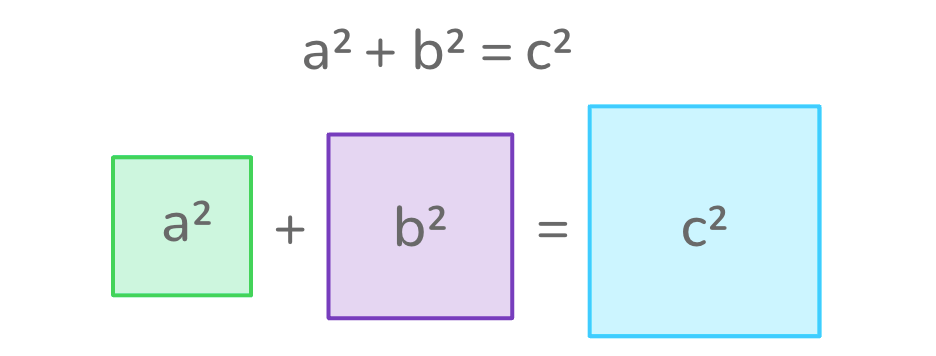
In this equation, “C” represents the longest side of a right triangle, called the hypotenuse. “A” and “B” represent the other two sides of the triangle.
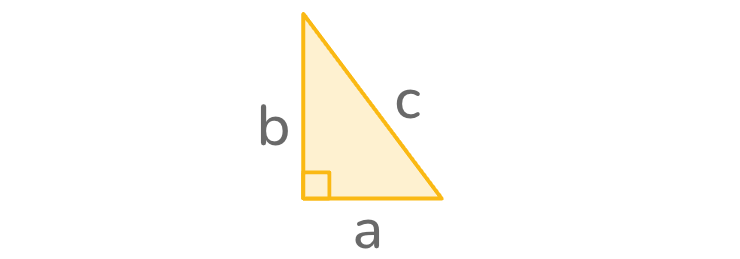
To use the Pythagorean theorem formula, we need to know the length of any two sides in a right triangle. We can then rearrange the formula to find the side we’re looking for.
So, if we take the formula:
a² + b² = c²
We can rearrange it to help us find the length we’re missing:
- To find the length of Side A: a² = c² – b²
- To find the length of Side B: b² = c² – a²
- To find the length of Side C: c² = a² + b²
This may sound complicated, but don’t worry! It’s easy to use once you know how. Let’s take a look at some examples.
How to use the Pythagorean theorem
Now that we know the Pythagorean theorem formula is, let’s talk about what we can use it for. The Pythagorean theorem can be used to solve for the hypotenuse or the shorter sides of a right triangle.
Finding the hypotenuse of a triangle
If we don’t know the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle (aka the longest side), we can work it out using Pythagoras’ theorem. The hypotenuse is represented by c in the Pythagorean theorem formula: a² + b² = c². By plugging in the given values of Side A and Side B, we can solve for the hypotenuse — Side C!
Let’s try an example!
Looking at the picture below, solve for Side C.
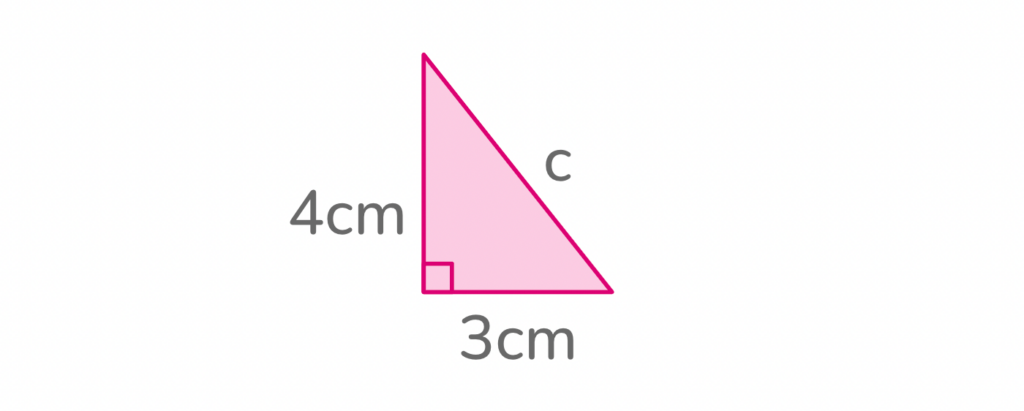
To start, we can flip the Pythagorean theorem equation to make it easier to read:
a² + b² = c² becomes c² = a² + b²
Next, plug the values of Side A and Side B into the equation since they are given. Side A = 4cm and Side B = 3cm. This gives us:
c² = 4² + 3²
Square Sides A and B to get:
c² = 16 + 9
Add 16 and 9 solve for a²:
c² = 25
Now we’re in the final stretch. We just need to find the square root of 25 to find the length of the hypotenuse (Side C)!
c² = √25
Therefore, the length of Side C = 5cm.
Finding the short side of a right triangle
We can also use Pythagoras’ theorem when we don’t know the length of one of the shorter sides of a right triangle.
We can rearrange the formula to help us find the side we don’t know. For example:
- If we don’t know Side A: a² = c² – b²
- If we don’t know Side B: b² = c² – a²
Let’s practice! In the example below, solve for Side A.
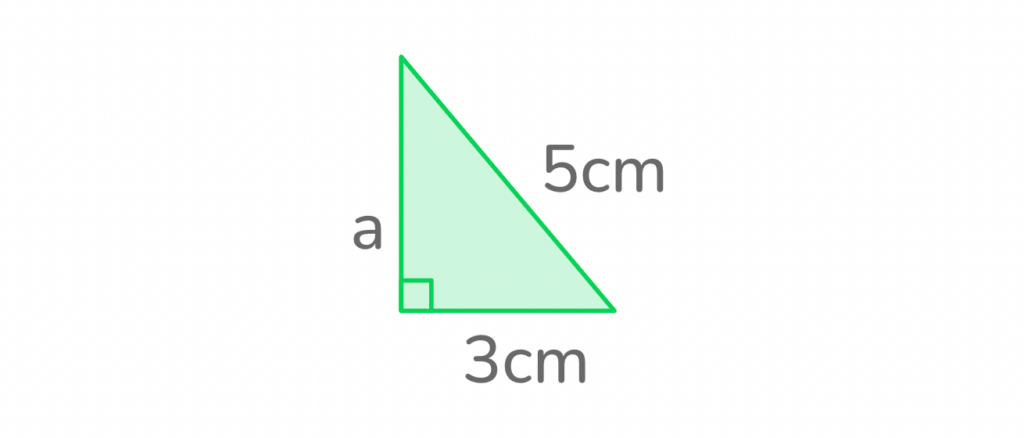
To work out the length of Side A, start by rearranging the formula to become:
a² = c² – b²
Next, plug in the values of Side C and Side B. (Remember: Side C is the hypotenuse!)
a² = 5² – 3²
Square Sides B and C to get:
a² = 25 – 9
Subtract 9 from 25 to solve for a²:
a² = 16
Now we’re nearly there! If we find the square root of 16, we’ll have our answer.
a = √16
Therefore, Side A = 4cm.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Pythagorean theorem examples
Ready to look at some more examples or have a go at using the theorem yourself? Take a look at the following practice problems with answers that follow!
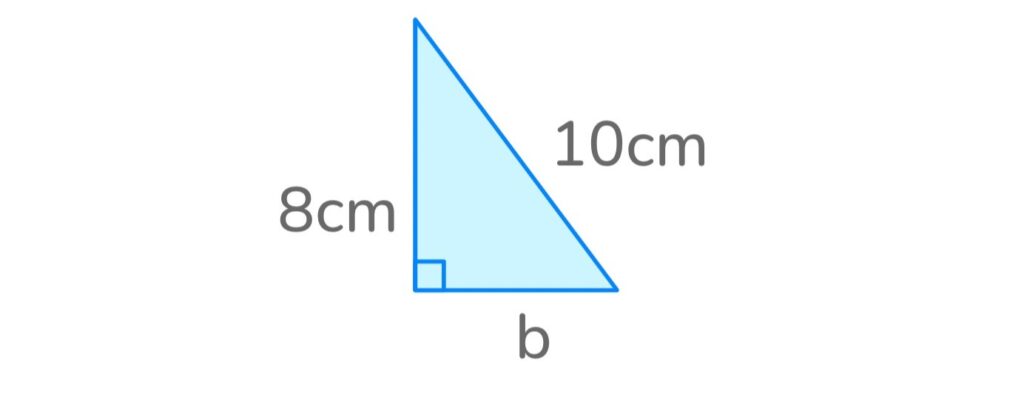
1. Find the length of b
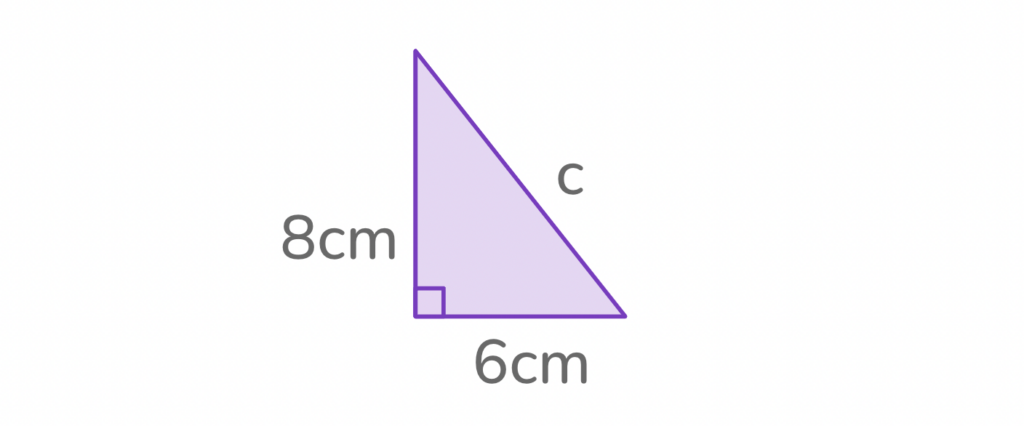
2. Find the length of C
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.

Answer Sheet
Question 1
Answer: 6cm
- Rearrange the formula to b² = c² – a²
- Plug in the values of Side C and Side A to get b² = 10² – 8²
- Square Sides A and C to get b² = 100 – 64
- Subtract 64 from 100 to get b² = 36
- Find the square root of b = √ 36 to solve for b
Therefore, b = 6cm.
Question 2
Answer: 10cm
- Flip the Pythagorean theorem formula to get c² = a² + b²
- Plug in the values of Side A and B to get c² = 8² + 6²
- Square Sides A and C to get c² = 64 + 36
- Add 64 and 36 to get c² = 100
- Find the square root of c = √ 100 to solve for c
Therefore, c = 10cm.