What Is a Quotient
Learn more about this important division term, and discover ways to find the quotient using simple subtraction methods.

Author
Jill Padfield
Published:
Oct 2024
Key takeaways
- The quotient comes in a couple forms – If one number is perfectly divisible by another, the quotients are likely whole numbers. But, if one number can’t be perfectly divided by another, the quotients are usually decimals.
- There are various ways to find it – You can use repeated subtraction or long division to find the quotient of any division problem.
- Remember the remainder – When a number is not perfectly divisible, include the remainder in your final answer!
Knowing how to find the quotient is a foundational math concept. It’s very simple — we divide one number by another, and the result is the quotient. Let’s dig in to learn more about the quotient, the forms it can take, and how to find it using subtraction skills.
What is a quotient in division?
When we divide one number by another number, we get the quotient. The quotient can be a whole number or integer, or, if the first number is not completely divisible, it can be a decimal. Some division problems even give a quotient with a remainder. There are a couple of different ways to find the quotient, too — let’s dive in to explore this concept with examples.
Definition of a quotient
The quotient in math is the number we get when we divide one number by another. For example, let’s take a look at the simple equation 6 ÷ 3 = 2. When we divide, we see that the result is 2.. So, 2 is the quotient. As a refresher, when talking about division, 6 is the dividend and 3 is the divisor.
Table of contents
Get math practice with DreamBox!
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Different forms of a quotient
A quotient can come in a variety of forms, such as whole numbers and decimals. Let’s look at a couple of examples!
Whole Numbers
When a number is perfectly divisible by another, the quotient is a whole number. For example, 24 ÷ 6 = 4. In this case, 24 is completely divisible by 6 and the whole number 4 is our quotient.
Decimal Numbers
When a number is not perfectly divisible by another number, the quotient is a decimal. For example, 16 ÷ 5 = 3.2. These types of division problems leave a remainder (R). This remainder is another way to find the quotient. You may also write this equation like:
16 ÷ 5 = 3 R 1 (quotient = 3 and remainder = 1)

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
How to find the quotient?
To find the quotient, you must divide two numbers. You can use repeated subtraction or long division — it’s up to you! Let’s break down each method.
Repeated Subtraction
Remember how to subtract? Some find subtraction easier and less overwhelming than division, and it can be helpful to think of division as a repeated subtraction problem. To find the quotient through repeated subtraction, subtract the divisor from the dividend until you get a 0 or until subtraction is no longer possible. Here, the number of times we subtract is the quotient.
Let’s do an example problem together!
Find the quotient of 40 ÷ 10 using repeated subtraction.

We subtracted 10 four times to get 0, so the 4 is the quotient.
Long Division Method
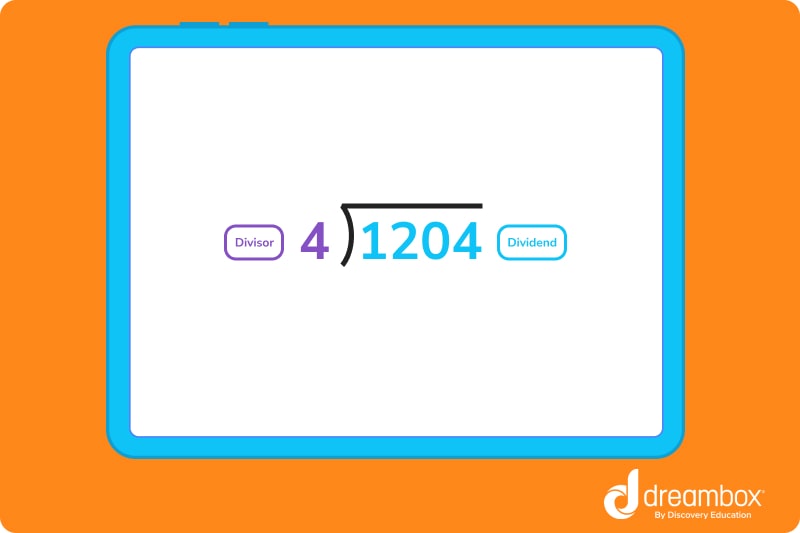
When finding the quotient in math using long division, we simplify the problem by dividing large numbers into groups or parts. To divide a number using this method, let’s draw a division house. Here, we write the divisor outside the division house, and the dividend inside the house. The quotient is written on top.
Here’s an example of what that looks like:
DMSBR is a helpful acronym to remember long division steps. DMSBR: divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, repeat. Want to have some fun memorizing it? Come up with your own words for each letter in the acronym!
Let’s do an example together with the steps written out:
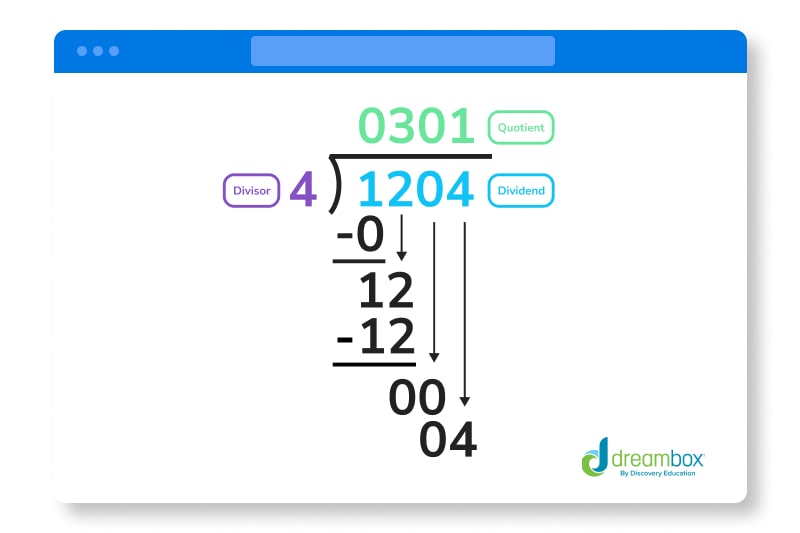
- Find the quotient of 1204 ÷ 4
- 4 goes into 1 zero times
- 1 – 0, 2 drops down
- 4 goes into 12 three times (first number of quotient is 3)
- 12 – 12 = 0, 0 drops down
- 4 goes into 0 zero times (second number of quotient is 0)
- 0 – 0 = 0, 4 drops down
- 4 goes into 4 one time (third number of quotient is 1)
- The quotient is 301. To check your answer, simply multiply 301 x 4 = 1204
Quotient and Remainder
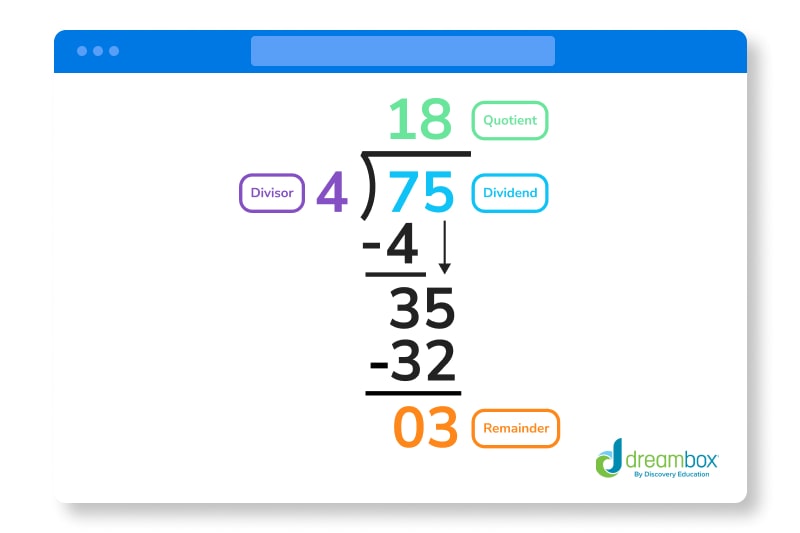
When using long division, not every divisor will divide equally. Oftentimes, you will have a leftover bit that can’t be divided any more. This is called your remainder, which is represented with an R hence the R in DMSBR.
Let’s take a look at an example of a long division problem that has a quotient with a remainder:
Find the quotient of 75 ÷ 4 using long division.
Let's Practice Together!
1. Find the quotient: 18 ÷ 6
Divide 18 by 6 to get 3. We know that a quotient is the number you get when you divide one number by another. So, the quotient is 3.
2. What is the quotient in this equation? 86 ÷ 2
Divide 86 by 2 to get 43. We know that a quotient is the number you get when you divide one number by another. So, the quotient is 43.
3. True or false. Quotients can be whole numbers or decimals.
True. Quotients can be whole numbers or decimals. Quotients can be decimals when a number is not completely divisible by another number.
Ready to give it a go?
- Now that we know what a quotient is and how to find it, we’re ready to do a few more practice problems to put our new skills to the test! Work through the following problems on your own. Feel free to look back at the practice problems above if you get stuck, or if you need a quick reminder on how to find the quotient.
Practice Problems
Click to reveal the answer.
The quotient is 6.
Divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, repeat.
The answer is 12.
The answer is 17 R 10
Parent Guide
-
1. The quotient is 6. How did we get here?
- 1. Divide 30 by 5 to get 6
2. We know that a quotient is the number you get when you divide one number by another.
3. The quotient of 30 ÷ 5 is 6. -
2. Divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, repeat. How did we get here?
- 1. We know that we use DMSBR to remember how to do long division.
2. Recall the steps of long division which include dividing, multiplying, subtracting, bringing down, and repeating until there are no numbers left. -
3. The answer is 12. How did we get here?
- 1. First, start by subtracting 12 from 144 to get 132. Continue to subtract 12 from the remaining number until you get 0 or can’t subtract 12 anymore.
2. 132 – 12 = 120
3. 120 – 12 = 108
4. 108 – 12 = 96
5. 96 – 12 = 84
6. 84 – 12 = 72
7. 72 – 12 = 60
8. 60 – 12 = 48
9. 48 – 12 = 36
10. 36 – 12 = 24
11. 24 – 12 = 12
12. 12 – 12 = 0
13. We subtracted 12 twelve times. So, 12 is the quotient. 144 ÷ 12 = 12. -
4. The answer is 17 R 10. How did we get here?
- 1. Set up your division house for the equation 435 ÷ 25.
2. The first number of the dividend, 4, is divided by the divisor, 25 which equals 0 with a remainder of 4.
3. The whole number result 0 is placed on top of the house. Ignore the remainders.
4. Next, the answer from the first operation is multiplied by the divisor, so 25 x 0 = 0. The result is placed under the divided number.
5. Now, take away the bottom number from the top number. 4 – 0 = 4
6. Bring down the next number of the dividend which is 3.
7. Divide the next number by the divisor. So, 43 ÷ 25 = 1 with a remainder of 18.
8. Place the whole number result, 1, on top. Ignore the remainders.
9. The answer from the above operation is multiplied by the divisor, so 25 x 1 = 25. Place the result under the last divided number.
10. Now take away the bottom number from the top number. 43 – 25 = 18
11. Bring down the next number from the dividend which is 5.
12. Divide the number by the divisor. 185 ÷ 25 = 7 with a remainder of 10.
13. Place 7 on top and ignore the remainder.
14. The answer from the above operation is multiplied by the divisor. 25 x 7 = 175. Place the result under the divided number.
15. Subtract the bottom number from the top number. 185 – 175 = 10
16. There is still 10 left over, but no more numbers to bring down.
17. The answer is 17 R 10 -
5. Brian can make 6 glasses of lemonade. How did we get here?
- 1. Brian has 24 total lemons.
2. He needs 4 lemons to make 1 glass of lemonade.
3. We can find how many glasses he can make with all of his lemons by taking 24 ÷ 4
4. 24 ÷ 4 = 6.
5. Brian can make 6 glasses of lemonade. 6 is the quotient.
FAQs about quotients
In math, the quotient is the result of dividing two numbers whereas the product is the result of multiplying two numbers.
When practicing your division skills, it’s important to know the terms. The most important are dividend, divisor, quotient, and remainder.
The quotient in math is the number we get when we divide one number by another. In perfect division, a quotient is a whole number with no remainder. But sometimes, a number can’t be perfectly divided, and there is a leftover number. This number is the remainder, and can often be expressed as a decimal number.
A helpful tip is to remember that the dividend equals the divisor multiplied by the quotient plus the remainder.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


About the Author
Jill Padfield
Jill Padfield has 7 years of experience teaching mathematics, ranging from Algebra 1 to Calculus. She is currently working as a Business Analyst, working to improve services for Veterans, while earning a masters degree in business administration.