What is skip counting?
Learning to skip count can help students improve their counting fluency and recognize number patterns. Let’s learn more about these benefits and how to skip count by several different numbers.

Author
Katie Wickliff
Published:
Oct 2024
Key takeaways
- • Skip counting can prepare students for multiplication and division.
- • Practicing skip counting through math games and activities is a fun way to help increase students’ mathematical confidence.
- • Skip counting helps increase overall number sense.
“Two, four, six, eight, who do we appreciate?!”
First chanted over 100 years ago, this catchy rhyme is a classic example of skip counting by 2s.
Skip counting is an incredibly useful mathematical skill that is often taught in the early elementary grades. By learning to skip count, students notice number patterns and increase their counting confidence. Being able to skip count sets students up for later multiplication and division success.
Table of contents
What is skip counting?
Skip counting is counting forward or backward by a number other than 1. When we skip count, we “skip over” a specific number of places in the counting sequence. Learning to skip count allows students to count more quickly and helps them recognize numbers in equal groups. Confident skip counting helps students learn to count money, tell time, and master multiplication and division.
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Types of skip counting
Forward skip counting
To forward skip count means to add the same number in a forward–or positive–direction. Let’s check out the example below:
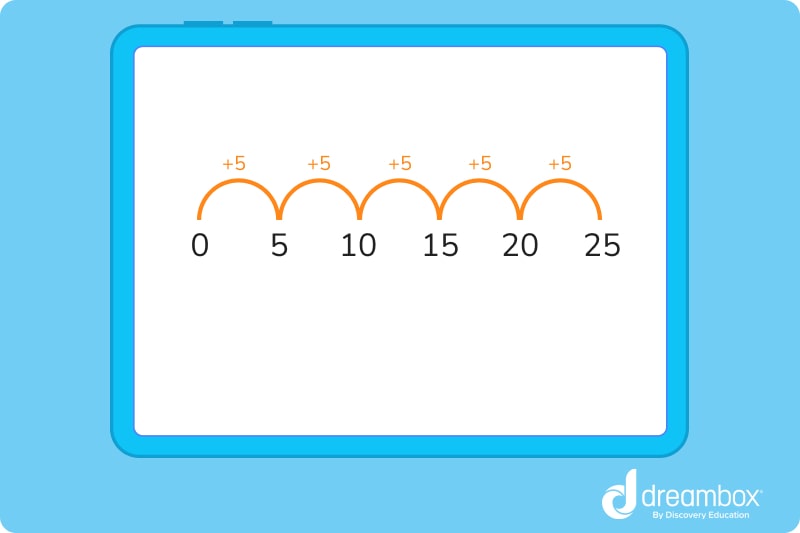
In this example, the number series begins at 0. Then, groups of 5 are added to move the number series in a positive direction.
Backward skip counting
To backward skip count means to subtract the same number in a backward, or negative, direction. Let’s check out the example below:
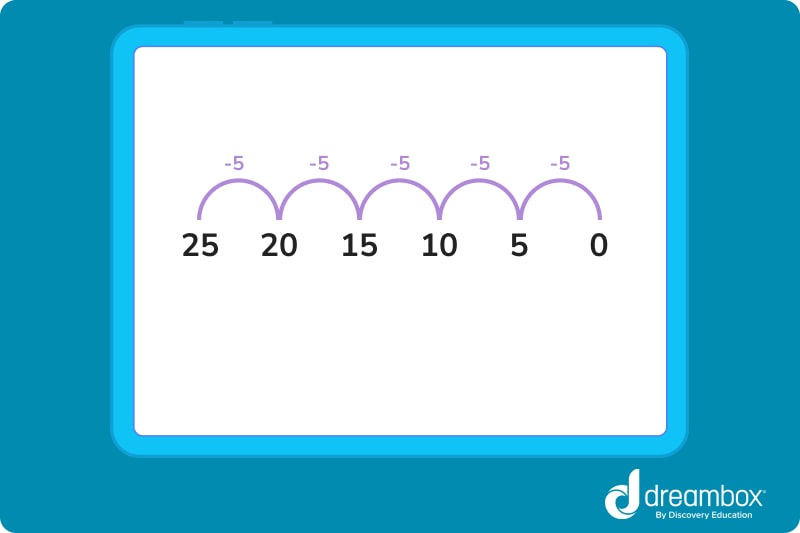
In this example, the number series begins at 25. Then, groups of 5 are subtracted to move the number series in a negative direction.
While the above examples skip count by 5s, you can use any whole number to skip count forward or backward. Students generally learn to skip count by 5s first and then start to notice patterns, such as two 5s make a 10.
Skip counting by 10s
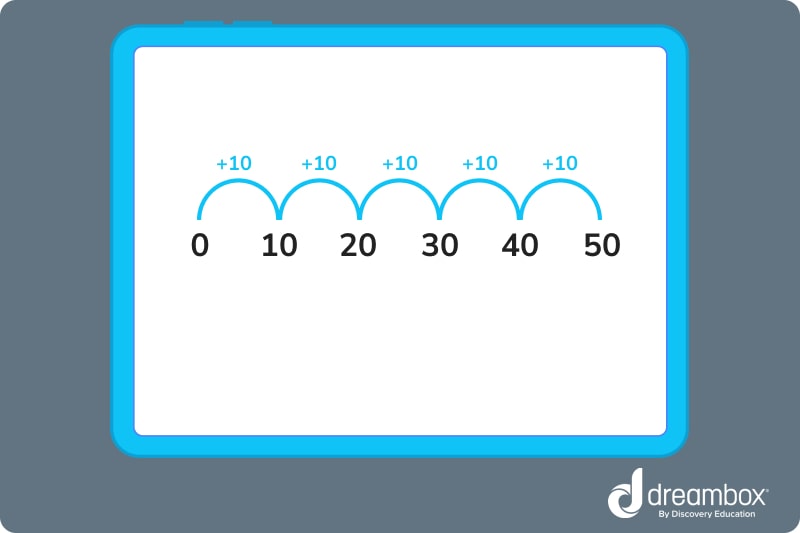
To skip count forward by 10s, add 10 from the starting number.
To skip count backward by 10s, subtract 10 from the starting number.
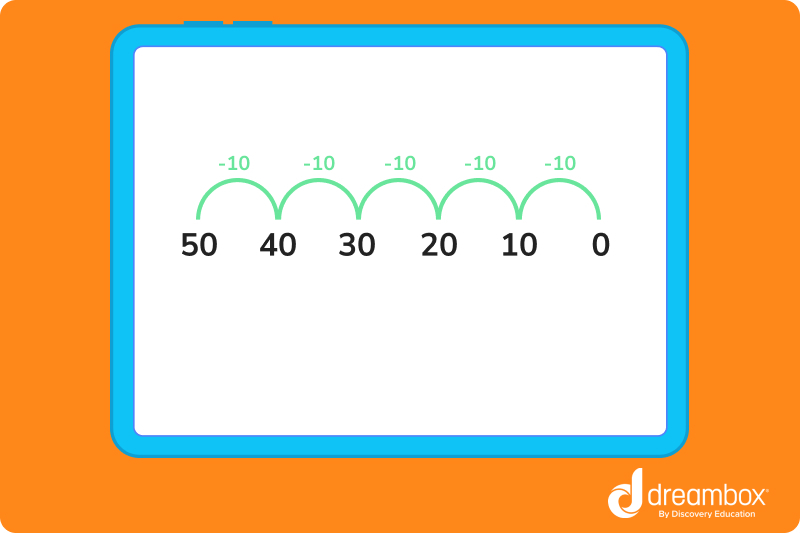
When skip counting by 10s, students will notice that the digit in the tens place increases by 1 each time they add 10 to a number. Noticing these patterns in skip counting helps develop number sense.
The ability to skip count by 5s and 10s sets up a solid foundation for learning to count money and tell time on an analog clock.
Additionally, once students understand how to skip count by 5s and 10s, other skip counting patterns become easier.
Skip counting by 2s
To skip count by twos, add 2 to any given number, just like the example below.
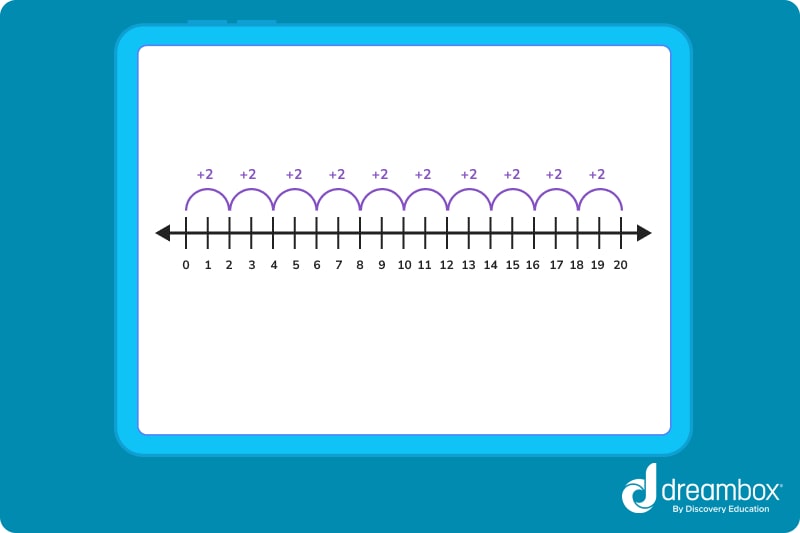
This number line shows forward skip counting by 2s, beginning at 0 and ending at 14. The number line is a useful visual when students learn to skip count because it allows them to see the numbers, including the ones they are “jumping over,” in sequence.
While many students learn to skip count by 10s, 5s, and 2s, skip counting shouldn’t stop there! Learning to skip count by 3 is a trickier pattern that students will be ready to tackle after they’ve mastered the basics. When your student is ready to skip count by 3s, 6s, 8s, or any other number, a skip counting chart is a helpful resource. Let’s look at an example:
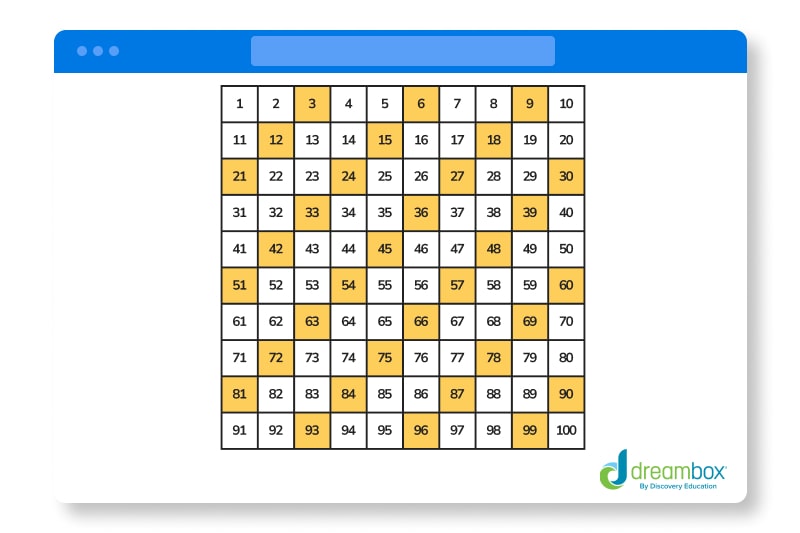
In this skip counting chart, every third square is colored yellow. Similar to using a number line, the colored skip counting chart allows the student to visualize each number. You can use a skip counting chart for any number. Also, DreamBox’s math practice app offers even more opportunity to practice skip counting skills.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Skip Counting Practice Problems
Q.1
Sam has 60 cookies and needs to skip count them by 10s. How many skips will he need to count to reach 60?
Quiz Complete!
You got 0 out of 5 questions correct.
Practice Problems
- 1. Sam has 60 cookies and needs to skip count them by 10s. How many skips will he need to count to reach 60?
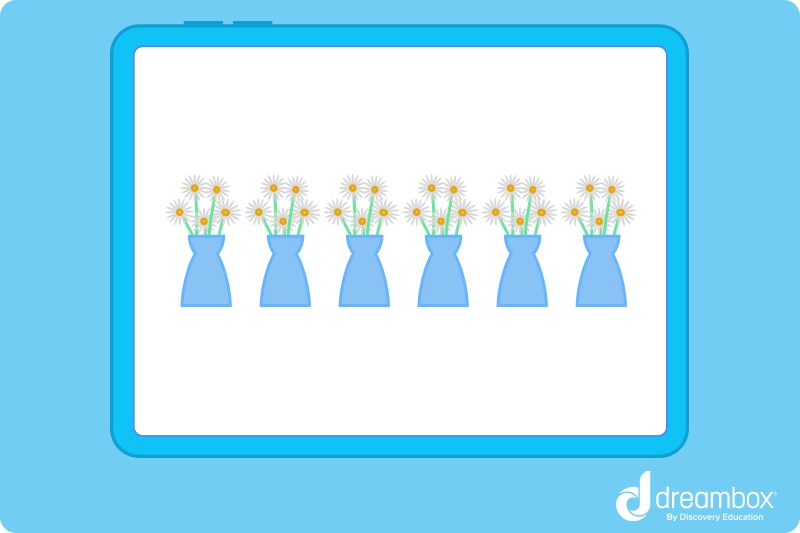
- 2. Look at the image below. Counting by 5s, how many flowers are there in total?

-
3. Which number sequence shows backward skip counting by 8 starting from 64?
A. 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64
B. 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24
C. 64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8, 0
D. 64, 60, 56, 52, 48, 44, 40, 36, 32
- 4. Marnie saw 4 bird nests in a tree. Each nest had 3 eggs in it. How many eggs did she see?
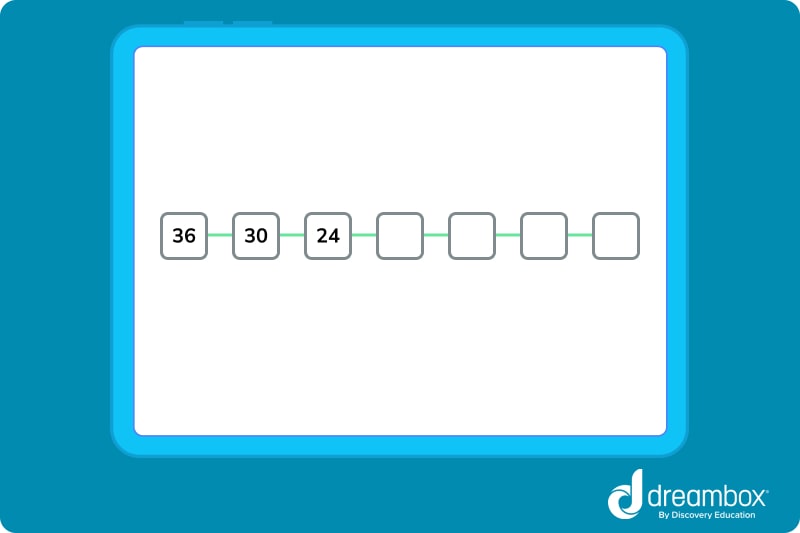
- 5. Look at the image below. Skip count backward by 6 to fill in the blanks.
Parent Guide
- 1. Sam needs to skip count by 10s to reach 60. His counting will look like this: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 So, Sam will skip count by 10s a total of 6 times to count the total number of cookies.
- 2. Counting by 5s will look like this: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 There are 30 total flowers.
- 3. C
-
4. Marnie needs to skip count by 3s for each of the 4 bird nests. Her counting will look like this:
3, 6, 9, 12
Marnie saw 12 total eggs. - 5. 18, 12, 6, 0
FAQs about Skip Counting
You can explain skip counting by saying it is a faster way of counting. To skip count, you simply “skip over” a specific amount of numbers. You can explain skip counting by first using small physical objects, such as groups of pennies, then moving on to using number lines or skip counting charts. You can also explain skip counting through rhymes, songs, and games.
While very young children can memorize skip counting rhymes and songs, children between the ages of 6 and 8 are usually ready to learn the concepts of skip counting.
Skip counting is usually introduced in kindergarten and expanded upon throughout elementary school.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


